Businesses must carefully choose production methods that maximize efficiency, reduce waste and meet evolving customer demands. Selecting the right production methods impacts not only operational costs but also quality, speed and adaptability. Manufacturers must evaluate how labor, machinery, materials and workflows are organized to consistently produce high-quality goods while remaining flexible to changes in demand or product design. The choice of production methods directly affects competitiveness, profitability and the ability to scale operations effectively.
Production methods vary widely, with some optimized for high-volume standardized output and others designed for custom, one-off items. Many companies combine multiple production methods in different areas of a facility to balance efficiency with flexibility. Staying informed about the advantages, limitations and best practices for each production method is essential to maintaining a competitive edge, optimizing resource use and ensuring customer satisfaction. Understanding these methods enables managers to implement processes that improve workflow, reduce errors and enhance overall production efficiency.
What Are Methods of Production?
Methods of production are the structured approaches and processes that manufacturers use to transform raw materials into finished goods. They encompass the organization of machinery, labor, materials and workflows to achieve consistent, high-quality output. The choice of production methods influences lead times, cost efficiency and the ability to respond to changes in demand or product specifications. By understanding the various production methods available, companies can select approaches that align with their strategic goals, scale efficiently and maximize resource utilization.
Production methods are not uniform and vary depending on product complexity, volume and customization needs. Some methods focus on high-volume production for standardized goods, while others prioritize flexibility for customized or project-specific items. Evaluating what production methods are and how they affect operations helps managers identify which processes are best suited to their products, resources and market demands. Effective production methods can improve efficiency, reduce waste and enhance employee productivity by providing clear workflows and measurable performance metrics.
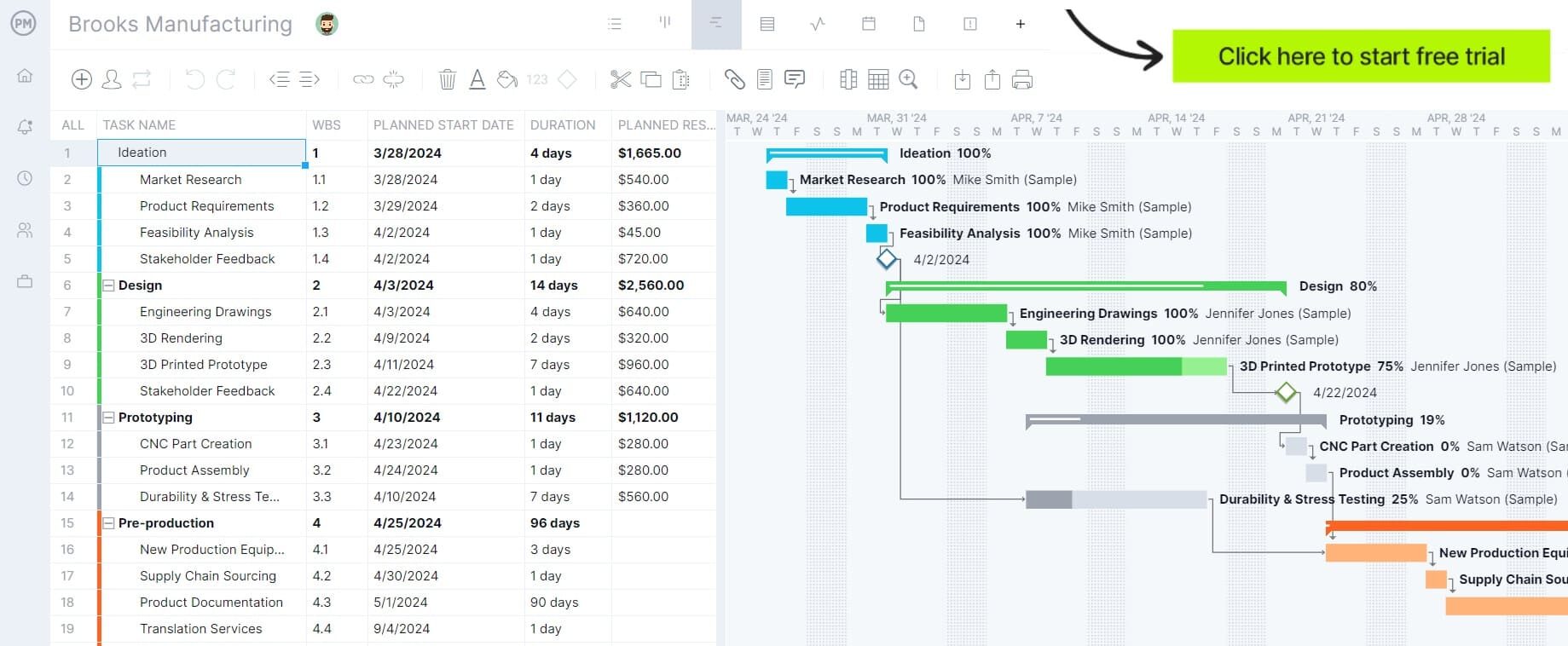
Project management software enhances production methods by centralizing planning, scheduling and tracking across operations. It allows managers to coordinate tasks, allocate resources and monitor production progress in real time. By visualizing workflows, identifying bottlenecks and tracking output against capacity, these tools provide actionable insights that optimize methods of production, reduce inefficiencies and support continuous improvement initiatives. Production teams can adjust schedules quickly, ensuring that products are delivered on time and within budget.
ProjectManager is a leading tool for managing production because it combines interactive Gantt charts with task lists, kanban boards and real-time dashboards. Managers can link task dependencies, assign resources, track milestones and monitor progress across multiple production lines. Customizable reports provide insights into costs, schedules and workload, helping teams refine production methods for maximum efficiency. With collaboration tools and real-time updates, ProjectManager ensures that manufacturing operations remain aligned, agile and productive. Get started with ProjectManager today for free

15 Top Methods of Production
Manufacturers use different production methods to meet specific operational needs, adapt to product complexity and manage costs. Each approach offers unique advantages in terms of flexibility, speed and scalability, making it essential to choose the right one for the type of product and demand level. Below are 15 top methods of production.
1. Job Production
Job production involves creating unique, custom products tailored to specific customer requirements. Each item is produced individually or in small quantities, making it highly flexible but labor-intensive. Examples include custom furniture, specialized machinery and bespoke clothing. Advantages include high customization and quality, while disadvantages include longer lead times and higher costs compared to standardized production. Job production is ideal when uniqueness and craftsmanship are more important than speed or volume.
2. Batch Production
Batch production produces a set quantity of identical items at one time before switching to a different product batch. This method balances efficiency and flexibility and is common in industries like food processing, textiles and pharmaceuticals. Advantages include the ability to manage inventory and reduce setup times, while disadvantages include downtime between batches and potential inefficiencies if demand fluctuates. Batch production allows manufacturers to respond to seasonal demand or product variations efficiently.
3. Mass Production
Mass production uses standardized processes and often automated machinery to produce large volumes of identical products. Examples include cars, electronics and consumer packaged goods. Mass production reduces per-unit costs and ensures consistency, but requires significant investment in machinery and infrastructure. It’s best suited for high-demand products with low customization. The primary advantage is efficiency, while the main limitation is inflexibility to changing specifications or custom orders.
4. Flow Production (Assembly Line Production)
Flow production organizes workstations sequentially, moving products continuously along a line. This method minimizes handling time and maximizes efficiency, making it ideal for large-volume manufacturing. Advantages include high throughput, consistent quality and predictable output. Disadvantages include high setup costs and limited flexibility. Examples include automotive assembly and electronics manufacturing, where consistent repetition and efficiency are key to meeting large-scale demand.

Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template to manage your projects better.
5. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing builds products layer by layer based on digital models. It enables rapid prototyping, customization and material efficiency. While slower than mass production for large volumes, it is highly flexible and cost-effective for small, complex designs. Examples include aerospace components, medical devices and custom tooling. The main advantages are design freedom and reduced material waste, while limitations include slower production times and higher unit costs for large-scale manufacturing.
6. Continuous Production
Continuous production operates 24/7 to produce products without interruption, commonly used in chemicals, steel and energy production. Advantages include maximum equipment utilization, high output and efficiency. Disadvantages include high setup costs, less flexibility and reliance on precise control systems. Continuous production is optimal when demand is consistent and predictable, and interruptions are costly.
7. Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing produces distinct items such as cars, electronics or appliances. Each product is identifiable and can be assembled from components. Advantages include flexibility for product variations and clear tracking of individual units. Disadvantages include potentially higher production costs and setup times. This method is widely used in industries requiring configurable products and traceable quality standards.
Related: 12 Best Production Scheduling Software for Manufacturing Projects in 2025
8. Lean Production
Lean production emphasizes reducing waste, improving efficiency and streamlining processes. It incorporates principles like just-in-time production, continuous improvement and employee involvement. Advantages include reduced operational costs and faster production cycles, while disadvantages include the need for strong coordination and disciplined management. Lean production is ideal for companies seeking efficiency without sacrificing quality.
9. Repetitive Manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing focuses on producing the same products continuously over long periods. Advantages include predictable output and efficient resource use, while disadvantages include limited flexibility for customization. Examples include household appliances and packaged goods. Repetitive manufacturing blends the benefits of mass production and flow production, ensuring consistent quality and output.
10. Flexible Manufacturing
Flexible manufacturing systems use automated machinery that can switch between products or configurations with minimal downtime. Advantages include the ability to adapt to changing customer demand and product variations. Disadvantages include higher initial investment and complexity. Examples include automotive plants producing multiple car models on the same line, benefiting from both efficiency and customization capabilities.
11. Project-Based Production
Project-based production focuses on unique, complex products requiring planning, coordination and milestone management. Advantages include customization and control over complex workflows. Disadvantages include longer lead times and higher costs. Examples include construction projects, shipbuilding and large-scale engineering initiatives. Effective project-based production requires meticulous planning, resource management and quality control to meet project objectives.
12. Make-to-Stock (MTS)
Make-to-stock produces goods based on anticipated demand, storing them as inventory. Advantages include fast delivery and meeting predictable demand. Disadvantages include the risk of overproduction or obsolete inventory. Examples include consumer packaged goods, clothing and electronics. MTS is ideal when demand is stable and forecasting is reliable, balancing inventory investment with customer service levels.
13. Make-to-Order (MTO)
Make-to-order produces items only after receiving a customer order. Advantages include reduced inventory costs and high customization. Disadvantages include longer lead times. Examples include custom machinery, tailored apparel and specialty food products. MTO ensures that production is closely aligned with actual demand, reducing waste and improving customer satisfaction.
14. Assemble-to-Order (ATO)
Assemble-to-order combines pre-manufactured components into finished products after receiving customer orders. Advantages include flexibility and faster delivery than MTO. Disadvantages include reliance on an accurate inventory of components. Examples include computers and modular furniture. ATO is useful when customers want product customization without the delays of full MTO production.
15. Engineer-to-Order (ETO)
Engineer-to-order produces fully customized products designed and engineered for specific client requirements. Advantages include uniqueness and high customer satisfaction. Disadvantages include long lead times, higher costs and extensive coordination. Examples include specialized machinery, ships and industrial equipment. ETO requires detailed planning, resource management and rigorous quality control to ensure each project meets client specifications.
Free Production Management Templates
While project management software is always better than static templates, we understand that not everyone is ready to upgrade. That’s why we have over 100 free project management templates on our site that can be downloaded immediately to help throughout your project. Here are just a few that are useful in production management.
Production Schedule Template
Download this free production schedule template to plan, assign and track manufacturing tasks. It outlines start and end dates for each task, assigns resources and tracks progress to keep production on schedule. Using templates improves visibility, coordination and accountability across teams and shifts.
Capacity Planning Template
Use this free capacity planning template to allow teams to forecast resource needs, evaluate workloads and identify bottlenecks. They help ensure that staff, machinery and materials are optimally utilized, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. By tracking available versus required capacity, managers can adjust schedules and allocate resources more efficiently.
Inventory Template
This free inventory template tracks raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods, providing insights into stock levels and supply chain efficiency. Maintaining accurate inventory records ensures that production is not interrupted by shortages while minimizing overstock, waste and associated carrying costs. Templates also support ordering, storage and logistics planning.
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Production Processes
ProjectManager provides multiple work management views, including task lists, kanban boards, calendars and Gantt charts, to organize production activities and monitor progress in real time. Managers can visualize workflows, assign resources, track deadlines and oversee multiple production lines simultaneously.
This visibility allows teams to spot delays or bottlenecks immediately, improving coordination and reducing errors. Employees can update progress and communicate directly within the platform, enhancing accountability and collaboration across all stages of production.
Robust Resource Planning and Cost Tracking
ProjectManager’s resource planning tools offer detailed insights into staff workloads, equipment usage and material allocation. Workload charts help balance assignments and prevent overloading, while allocation can be based on availability, skill sets and task priorities.
Cost tracking dashboards allow managers to monitor labor hours, material expenses and project budgets in real time. By integrating scheduling, resource planning and financial tracking, teams can optimize production throughput, reduce waste and maintain profitability across all production methods.
Real-Time Dashboards and Reports
Dashboards provide an at-a-glance view of production health, resource utilization, task progress and key performance metrics. Customizable reports allow managers to analyze trends, evaluate performance against goals and make data-driven adjustments to improve efficiency.
Graphs and charts visually represent workload distribution, production output and cost utilization, giving teams actionable insights. By leveraging dashboards and reports, ProjectManager enables continuous monitoring, evaluation and optimization of production processes, ensuring operations remain efficient, agile and aligned with business objectives.
Related Production Management Content
For readers who want to learn more about manufacturing beyond the methods of production, check out the links below. They take you to articles on production scheduling, tracking and more.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.