First, let’s get an intuitive feel for what probabilities mean in the world of robot localization.
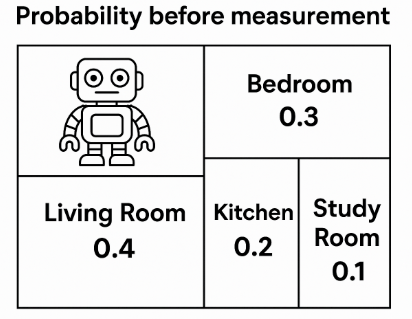
Imagine a home with four rooms: a Living Room, Bedroom, Kitchen, and Study Room. The robot doesn’t know exactly where it is, but it can estimate the likelihood of being in each room based on past experience or initial belief.
For example, it might estimate:
- Living Room:
0.4 - Bedroom:
0.3 - Kitchen:
0.2 - Study Room:
0.1
These probabilities reflect the robot’s confidence in being in each room. And since it knows it must be somewhere, the total always adds up to 1.
Think of it like a robot’s inner thought:
“I’m probably in the living room… but I might be in the kitchen too.”
Taking a Measurement
“I need to do a measurement to find out where I really am” The robot thinks, then it scans its surroundings and sees a bed.
From past training or programming, it knows:
- Beds are very likely to appear in the Bedroom , for example given bedroom, the chance of having a bed is (Bed|Bedroom) = 0.7
- Rarely appear in the Study Room or Living Room, for example given Study Room or Living Room, the chance of having a bed is (Bed|Study Room) = 0.2, (Bed|Living Room)=0.2
- Almost never appear in the Kitchen, for example (Bed|Kitchen)=0.05
Update Probabilities:
Robot then update its belief using this new observation. This is where Bayes’ Rule comes in.
The formula of Bayes’ theorem is:
P(A | B) = [P(B | A) × P(A)] / P(B)
In our case, we are trying to figure out the probability that the robot is in a specific room given that it observed a bed, as P(Room∣Bed)
Because P(B) in our case is the total probability of observing a bed, which isn’t specific to any single room. We can calculate it by assuming over all possible rooms:
P(Bed) = ∑ [P(Bed | Roomᵢ) × P(Roomᵢ)] ,
We can noted 1/P(Bed) as η, and receive:
P(Room∣Bed) = η ⋅ P(Bed∣Room) ⋅ P(Room)
Intuitively, the updated belief is “ how likely it was to see a bed in each room” multiply “how likely it thought it was in that room before the measurement”.
Example of how to calculate the probability of P(bedroom | bed):
Step 1: Prior Beliefs P(Room)
P(Living Room) → 0.4
* P(Bedroom) → 0.3
P(Kitchen )→ 0.2
P(Study Room) → 0.1
Step 2: Likelihoods P(Bed | Room)
*P(Bed | Bedroom) = 0.7
P(Bed | Living Room) = 0.2
P(Bed | Study Room) = 0.2
P(Bed | Kitchen) = 0.05
Step 3: Apply Bayes’ Theorem
P(Room | Bed) = [P(Bed | Room) × P(Room)] / P(Bed)
P(Bedroom | Bed) = [0.7 × 0.3] / P(Bed) = 0.21 / P(Bed)
Step 4: Compute the Evidence P(Bed)
P(Bed) = ∑ [P(Bed | Roomᵢ) × P(Roomᵢ)]
P(Bed) = (0.7 × 0.3) + (0.2 × 0.4) + (0.05 × 0.2) + (0.2 × 0.1)
= 0.21 + 0.08 + 0.01 + 0.02
= 0.32
✅ Final Calculation
P(Bedroom | Bed) = 0.21 / 0.32 ≈ 0.656
So after seeing a bed, the robot becomes 65.6% confident it’s in the Bedroom, up from just 30% before the observation.
Here is an interesting video explaining Bayes’ theorem: