A project schedule keeps everything moving on time, which is why schedule planning is one of the most important parts of project management. It’s not just about making a calendar—it’s about following a process to define, sequence and estimate the time for all project activities. In this blog, we’ll explain what schedule planning is, why it matters and when it should be done.
What Is Schedule Planning in Project Management?
Schedule planning in project management is the process of defining how and when project activities will be carried out. It involves identifying tasks, estimating their durations and sequencing them into a logical order. The result is a timeline that outlines the entire project from start to finish. This plan ensures tasks are completed on time, resources are properly allocated and stakeholders have a clear understanding of how the project will progress.
Gantt charts help in project schedule planning by visually mapping out tasks, durations, dependencies and deadlines across a timeline. In project management, this makes it easier to see the sequence of work, allocate resources and identify the critical path—the chain of tasks that directly impacts the project’s finish date.
Gantt charts also allow for quick adjustments when delays occur, helping teams maintain realistic schedules and coordinate efforts effectively. By providing a clear, interactive overview of the entire project plan, Gantt charts improve planning accuracy, communication and on-time delivery.
Scheduling planning software facilitates this process. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that has robust Gantt charts for schedule planning. Our Gantt charts make it easy to schedule tasks, resources and costs, but that’s only the start. By linking all four types of task dependencies, project managers help avoid cost overruns and bottlenecks. It’s simple to filter for the critical path to identify those tasks with zero slack. Then, set a baseline to track the project in real time. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Why Is Schedule Planning Important?
Schedule planning ensures projects are delivered on time, within scope and under budget. Without a proper schedule, teams can become disorganized, deadlines get missed and resources are misused. A well-structured schedule provides visibility, sets expectations and helps manage risks. It allows for better coordination between tasks and team members, improves stakeholder communication and forms the foundation for monitoring and controlling progress throughout the project lifecycle.
When Should Schedule Planning Be Done?
The schedule planning process starts early in the project lifecycle, often during the initiation phase. At this stage, a preliminary or tentative schedule is created to provide a high-level overview of the project’s estimated duration.
This rough timeline is typically included in the project charter and is based on assumptions, early requirements and known constraints. Its purpose is to set initial expectations and support early stakeholder alignment.
A more detailed and accurate project schedule is developed during the project planning phase. This version incorporates refined task definitions, time estimates and dependencies, providing a solid framework to guide execution and control. The transition from tentative to detailed scheduling is essential for maintaining project momentum and ensuring that planning evolves with clarity and precision.
Schedule Planning Techniques
Schedule planning techniques help project managers estimate durations, sequence tasks and create realistic timelines. These methods include visual tools and mathematical models that support better planning and coordination. In the sections below, we’ll cover key techniques like the critical path method (CPM), PERT charts and other approaches to build effective project schedules.
Critical Path Method
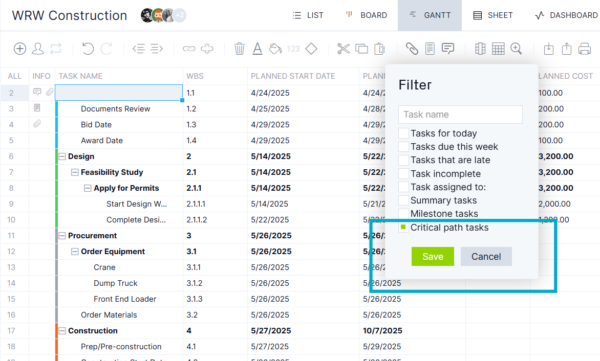
The critical path method (CPM) is a schedule planning technique that uses a network diagram to map task sequences and dependencies. Each activity is connected based on its logical relationship to others, forming a path through the project. CPM identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks—the critical path—which determines the shortest possible project duration.
Project managers use mathematical calculations to estimate start and finish dates and to calculate float for non-critical tasks. By visualizing the task flow, CPM helps prioritize activities, allocate resources effectively and predict how delays will affect the overall project timeline. Below is an example of the critical path method using the variables of the critical path algorithm, which are the earliest start time (ES), latest start time (LS), earliest finish time (EF), latest finish time (LF) and slack.


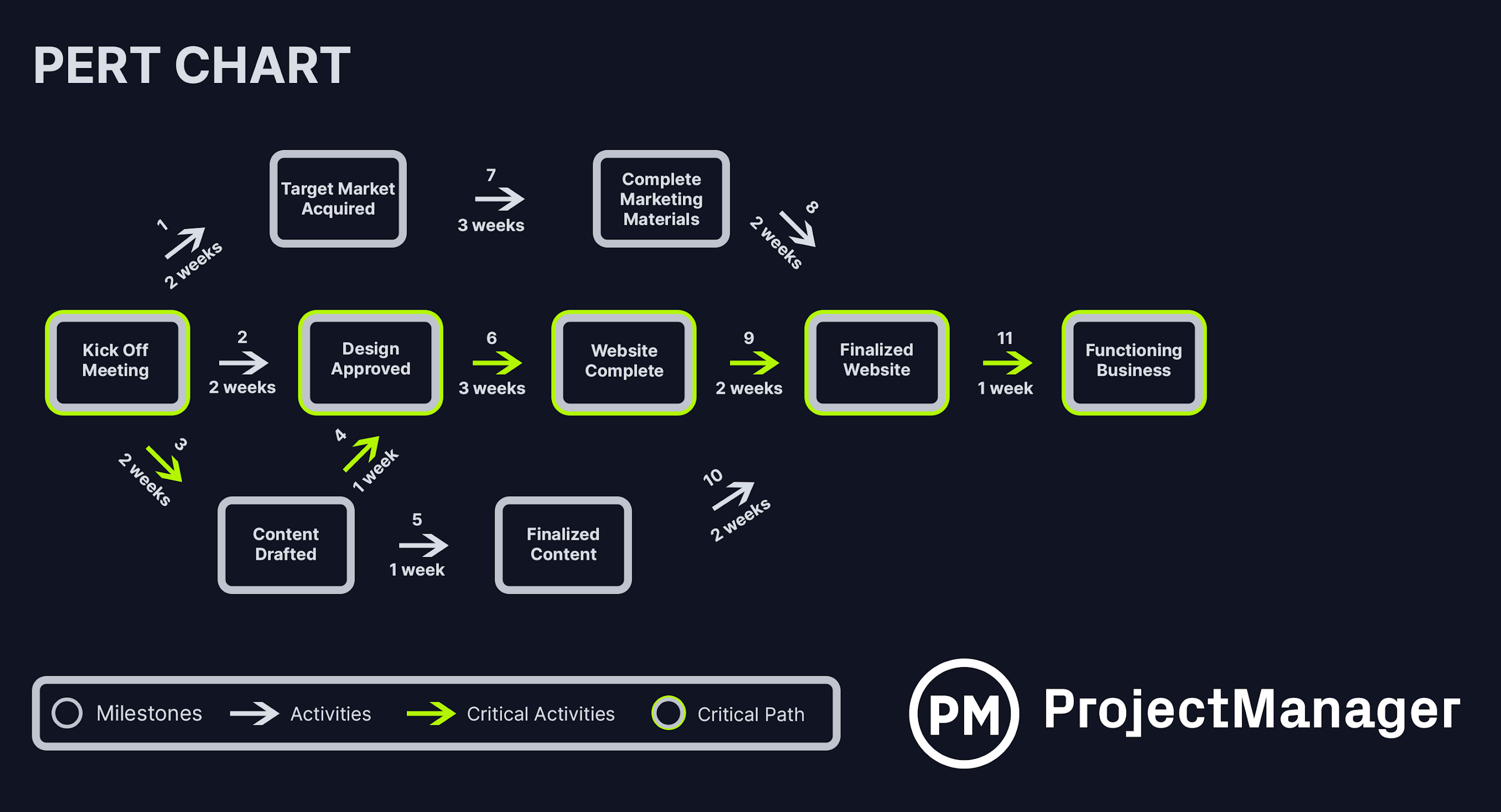
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
The program evaluation and review technique (PERT) also uses a network diagram to visualize task sequences and dependencies, but it’s specifically designed for uncertain timelines. For each task, project managers estimate three durations: optimistic, pessimistic and most likely. These estimates are then used to calculate an expected duration using weighted averages.
PERT is useful when detailed information is lacking and tasks involve high uncertainty. The resulting schedule offers a probabilistic view of the total project duration, helping teams prepare for variability and make more informed decisions about resource allocation and timeline expectations. To try this technique, download our free PERT chart template for Excel.

Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning is a progressive elaboration technique used in schedule planning when parts of the project are unclear or likely to change. In this approach, near-term tasks are planned in detail while future work is outlined at a higher level. As the project progresses and more information becomes available, future activities are broken down and scheduled in greater detail.
This method allows teams to move forward without waiting for every detail to be known. It’s especially helpful in complex or evolving projects where flexibility and adaptability are necessary for effective scheduling and task management.
Project Fast Tracking
Project fast tracking is a schedule compression technique that involves performing tasks in parallel that were originally planned to be done sequentially. This method is typically used during project execution to recover lost time or accelerate delivery. Fast tracking helps reduce the overall project duration but also introduces risk, as overlapping tasks may lead to coordination issues or rework.
Effective fast tracking requires a thorough understanding of task dependencies and close communication among teams. When used carefully, it’s a powerful tool for keeping a project on schedule or meeting urgent deadlines without immediately increasing resource costs.
Project Crashing
Project crashing is another schedule compression technique used during project execution to shorten the project timeline by adding extra resources. This could mean assigning more team members, paying for expedited deliveries or working overtime. Crashing focuses on critical path activities to ensure time gains directly impact the overall duration.
While effective, it often increases project costs and should be used strategically. It’s typically implemented when fast tracking isn’t enough or when a deadline must be met at all costs. Proper planning and cost-benefit analysis are essential when deciding which tasks to crash and how to do so efficiently.
Related: 15 Best Project Scheduling Templates for Excel
Steps in the Schedule Planning Process
Schedule planning is a structured process that begins during the project initiation phase and continues through the planning, execution and monitoring and control phases. Each step builds upon the previous one to create a complete, actionable timeline. The process involves identifying tasks, visualizing timelines, and refining the schedule as more information becomes available or changes occur during project delivery. We illustrate some of these steps with screenshots from ProjectManager for clarity.
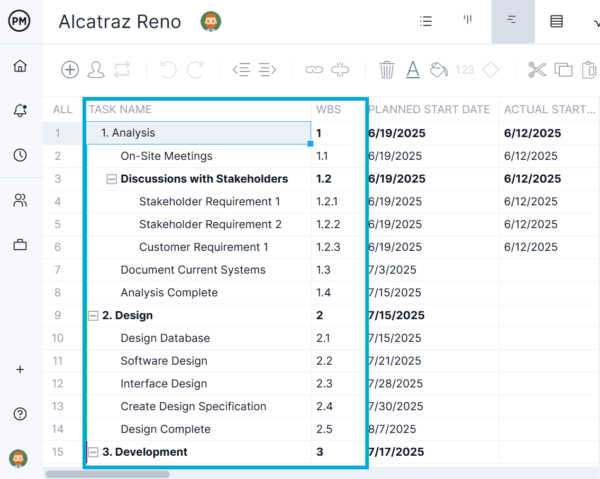
1. Create a Work Breakdown Structure
The first step in schedule planning is to create a work breakdown structure (WBS). This tool breaks down the entire project into smaller, more manageable components. Tasks are grouped into deliverables, sub-deliverables and work packages, which are organized in a hierarchical structure.
The WBS ensures that all work is identified and accounted for. It helps teams visualize the full scope of the project, making it easier to assign responsibilities, define durations and prepare for sequencing. A complete WBS lays the foundation for developing an accurate schedule in the next steps of the planning process.
2. Visualize the Project Timeline with CPM or PERT Diagrams
Using a network diagram, such as a critical path method (CPM) or program evaluation and review technique (PERT) chart, is vital in developing a project schedule. These diagrams help teams understand the logical flow of tasks and visualize the full project timeline from start to finish.
They highlight task dependencies and identify the critical path, making it easier to spot which activities directly impact the project’s total duration. By providing a clear visual representation, network diagrams help project managers prioritize tasks, allocate resources more effectively and develop a schedule that accounts for fixed and flexible elements. These tools also enhance communication by giving stakeholders a shared understanding of how the project will unfold.
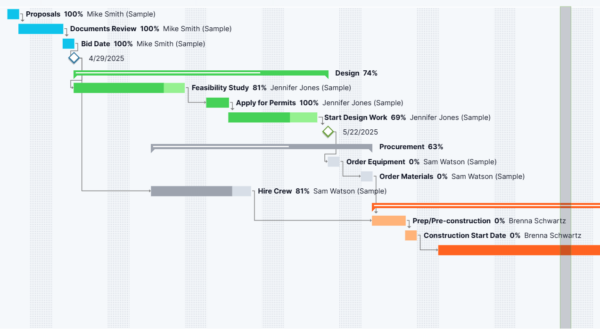
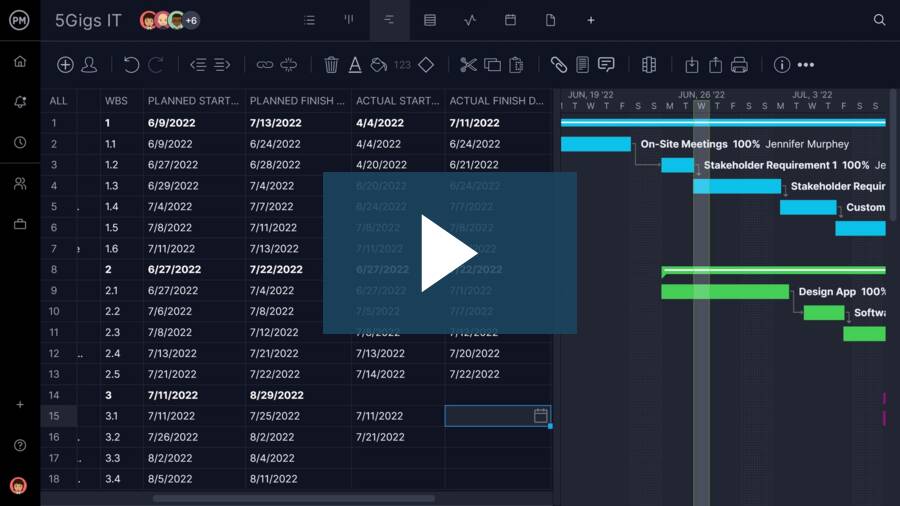
3. Make a Project Schedule with a Gantt Chart
Once tasks and dependencies are defined, you can build a project schedule using a Gantt chart. On the left side of the Gantt chart is the task grid, where you input task details such as duration, start and finish dates, assigned team members, required resources and estimated costs.
On the right side is the Gantt timeline, a horizontal stacked bar chart that maps tasks across a calendar. Each bar represents a task’s duration, clearly showing start and end points and overlaps. This format provides a visual overview of the entire schedule, helping teams track progress, monitor deadlines and manage workloads. Gantt charts are essential tools for day-to-day execution and schedule adjustments.
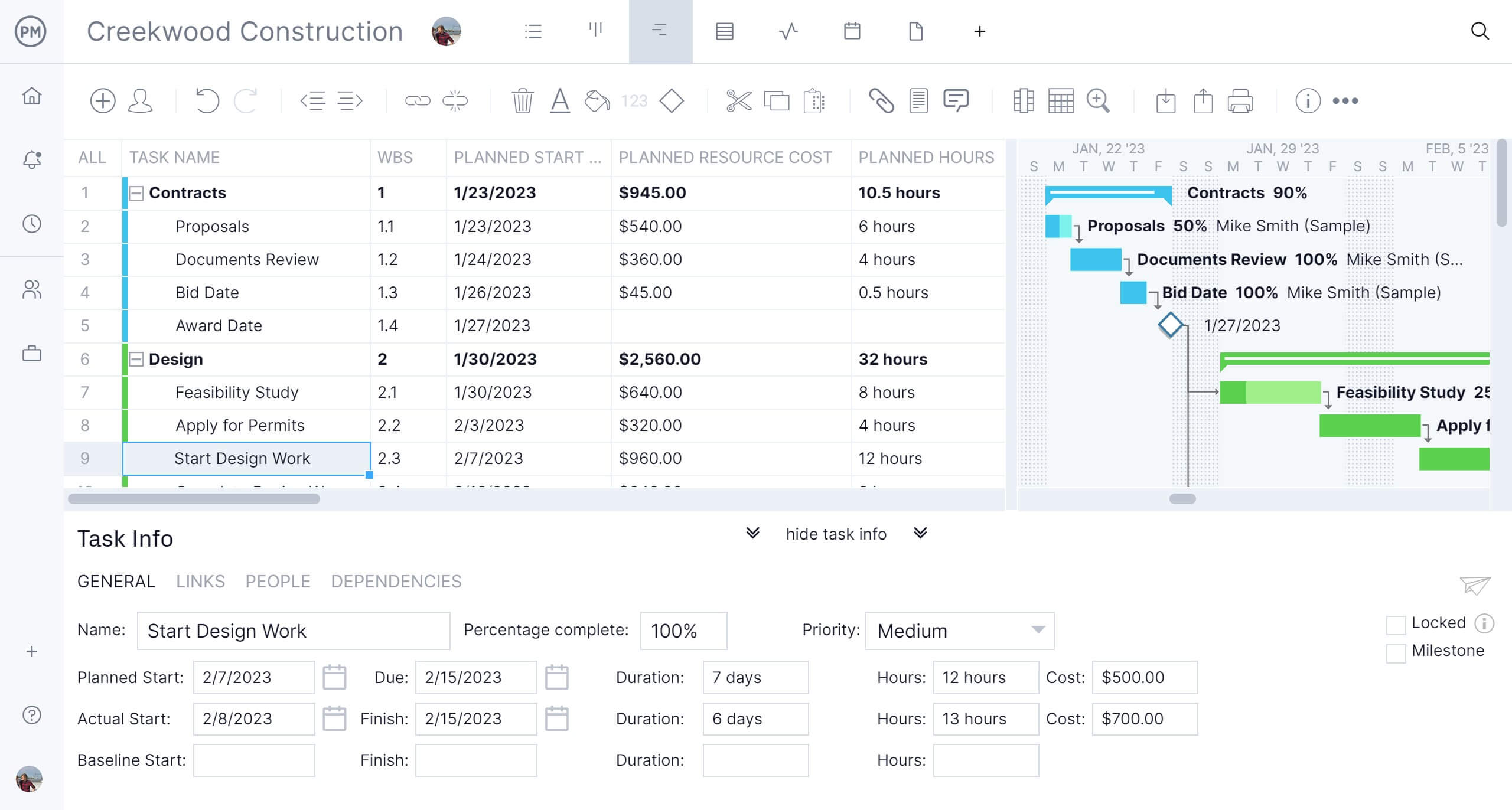
4. Make a Schedule Management Plan
The schedule management plan is a formal document that outlines how the project schedule will be developed, monitored and controlled throughout the project lifecycle. It defines the scheduling methodology, tools, update frequency and thresholds for acceptable performance.
This plan also establishes how changes to the schedule will be evaluated and approved, as well as how progress will be communicated to stakeholders. Within the context of schedule planning, the schedule management plan ensures consistency, accountability and transparency. It allows project teams to align expectations, minimize confusion and proactively manage risks. Documenting the procedures for managing the schedule provides a structured approach to maintaining control over timelines and supports informed decision-making as the project evolves, especially when adjustments become necessary during execution.
5. Adjust the Project Schedule During the Project Execution Phase
During the execution phase, real-world conditions often force adjustments to the project schedule. These changes may stem from shifting resource availability, contractor delays, client requests or unexpected events. Project managers must respond quickly by reassessing timelines, resequencing tasks or updating dependencies.
In some cases, schedule compression techniques like fast tracking or crashing may be applied to maintain deadlines. Ongoing monitoring also reveals variances that must be addressed to stay aligned with objectives. Gantt charts and project dashboards play a critical role in visualizing changes and reassigning workloads efficiently. Flexibility and responsiveness are essential during execution, and maintaining an up-to-date schedule helps ensure coordination, manage stakeholder expectations and minimize disruptions that could compromise project success.
Want to learn even more about tools that support schedule planning? Watch our video on project scheduling software below.
Who Is Responsible for Schedule Planning?
The project manager is primarily responsible for schedule planning. They define the approach, develop the timeline and oversee adjustments throughout the project. However, other stakeholders also influence the process. The project sponsor provides high-level direction and approves major scheduling decisions, while the project client may request changes that impact the timeline.
Team leads and subject matter experts contribute by estimating task durations and identifying dependencies. Procurement and resource managers also provide input based on availability and constraints. Successful schedule planning depends on collaboration among all involved parties to build a realistic, achievable and well-aligned project timeline.
Free Schedule Planning Templates
For those not ready to upgrade to project management software, there is another way for you to schedule planning in your project. We offer over 100 free project management templates for Excel and Word that help with every aspect of managing projects. Below are just a few that can help when scheduling that project.
Gantt Chart Template
Download this free Gantt chart template to organize project tasks and durations in a visual bar chart format. It helps with schedule planning by laying out what needs to be done, when and in what order, making it easy to set deadlines, track progress and adjust plans as needed. This clear visualization improves coordination, prevents scheduling conflicts and keeps the project on track.
Critical Path Template
Use this free critical path template to map out the sequence of dependent tasks that determine the shortest possible project duration. It helps with schedule planning by identifying which tasks must stay on track to avoid delaying the entire project. By highlighting these critical tasks and showing where there’s scheduling flexibility, the template allows managers to prioritize resources, anticipate risks and maintain tighter control over the project timeline.
PERT Chart Template
This free PERT chart template is a visual project management tool that maps out tasks, timelines and dependencies using nodes and arrows, along with three time estimates—optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely—for each task. It helps with schedule planning by accounting for uncertainty in task durations, allowing managers to calculate more realistic project timelines and identify critical paths. This leads to better risk management, more accurate scheduling and improved decision-making under uncertainty.
ProjectManager Is Advanced Schedule Planning Software
Instead of templates, which are static documents that pull project managers and their teams away from more important tasks, upgrade to ProjectManager, advanced schedule planning software that empowers teams with real-time dashboards and customizable reports to keep projects on track and informed at every stage.
Its live dashboard automatically pulls data from tasks, timesheets and resource usage to provide instant visibility into progress, deadlines, and performance metrics—without manual updates. Customizable reports allow users to drill into specific schedule details, such as task status, variance from plan and critical milestones, offering data-driven insights that support better forecasting, faster adjustments and stakeholder confidence. Together, these tools turn scheduling into a continuously optimized, insight-led process.
Schedule on Multiple Project Scheduling Views
ProjectManager enhances schedule planning by offering multiple project views—including Gantt charts, task lists, kanban boards, sheet views and calendars—that all sync in real time. This flexibility lets teams plan and manage schedules in the format that suits their workflow while keeping everyone aligned.
Project managers can build detailed timelines and dependencies in the Gantt view, while team members track their tasks in list or board views, and deadlines appear in the shared calendar. Any change made in one view—like shifting a task deadline or updating progress—automatically updates across all others, ensuring consistent, up-to-date scheduling from every angle.
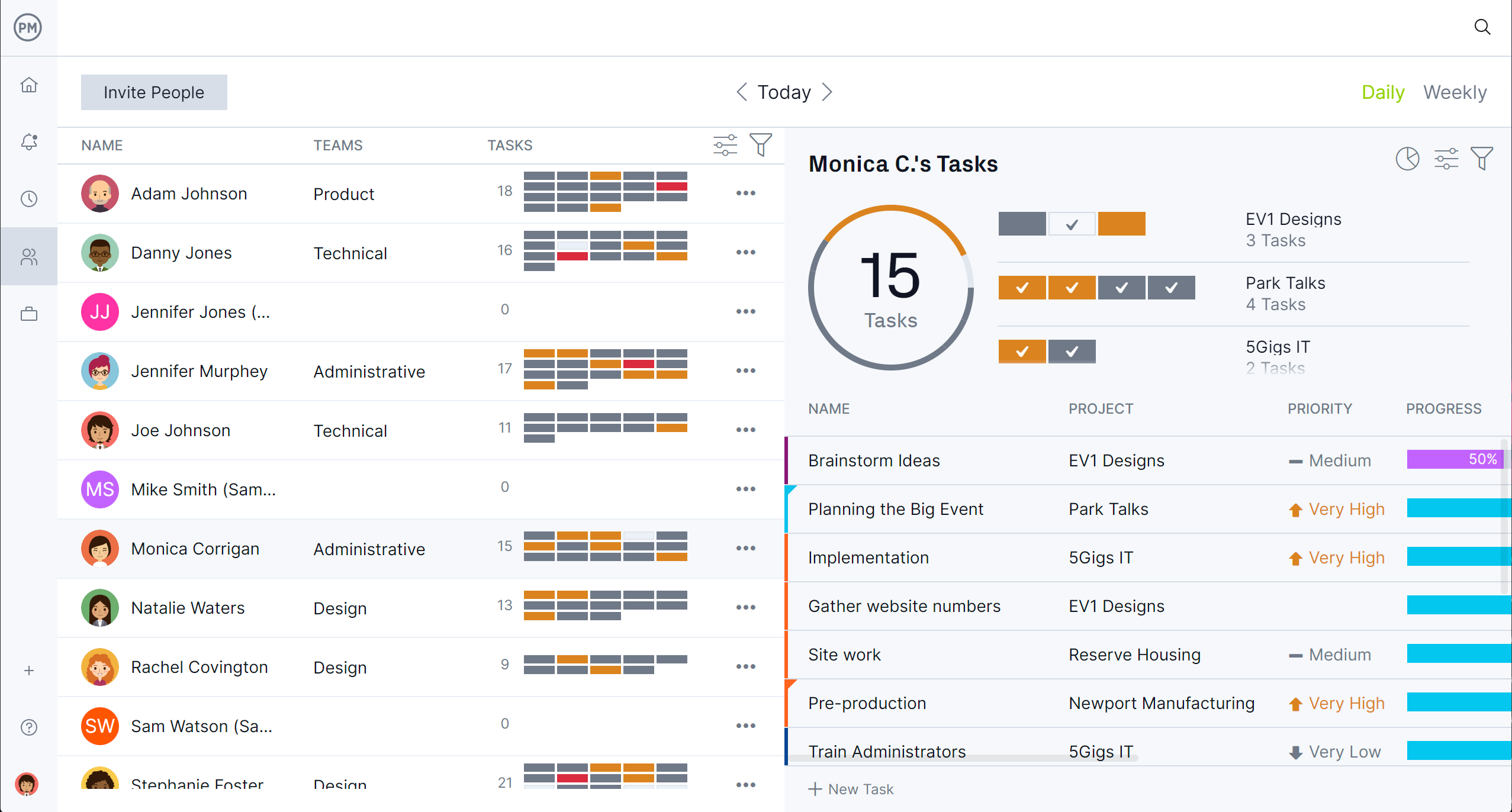
Manage Schedule Planning With Resources and Cost Tracking Tools
ProjectManager’s resource and cost tracking tools support schedule planning by aligning workforce availability and budget constraints with project timelines. Resource management features like the team page let you assign tasks based on team capacity and skill sets, while the workload chart ensures no one is overbooked, helping to create realistic schedules that prevent delays.
At the same time, cost tracking tools like our secure timesheets monitor labor rates, material expenses and other project costs in real time. This integration ensures that schedule plans are financially viable and adaptable, allowing project managers to adjust tasks, timelines or resources proactively to stay on budget and on schedule.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.