Effective production forecasting is crucial for manufacturing businesses seeking to remain competitive and responsive in a rapidly evolving market. When done correctly, it helps align inventory, staffing, and scheduling with actual demand, allowing companies to avoid costly overproduction or shortages.
In this blog, we’ll break down the basics of production forecasting and show how it supports smarter decision-making across operations. Whether you’re managing a small facility or a global supply chain, understanding forecasting fundamentals is key to improving efficiency and profitability.
What Is Production Forecasting?
Production forecasting is the process of predicting future manufacturing output based on historical data, market trends and customer demand. It helps manufacturers plan how much to produce, when to produce it and what resources will be needed. Accurate forecasting ensures that production levels align with demand, reducing waste, avoiding stockouts and improving overall efficiency. It supports key decisions around labor scheduling, raw material procurement and equipment usage.
Forecasting is not a one-time task—it’s an ongoing process that must adapt to shifting market conditions, supply chain disruptions and internal capacity changes. By analyzing sales patterns, order history and seasonal trends, production teams can build more reliable forecasts and adjust production schedules accordingly. The better the forecast, the more streamlined the operations, leading to fewer delays and improved cost control.
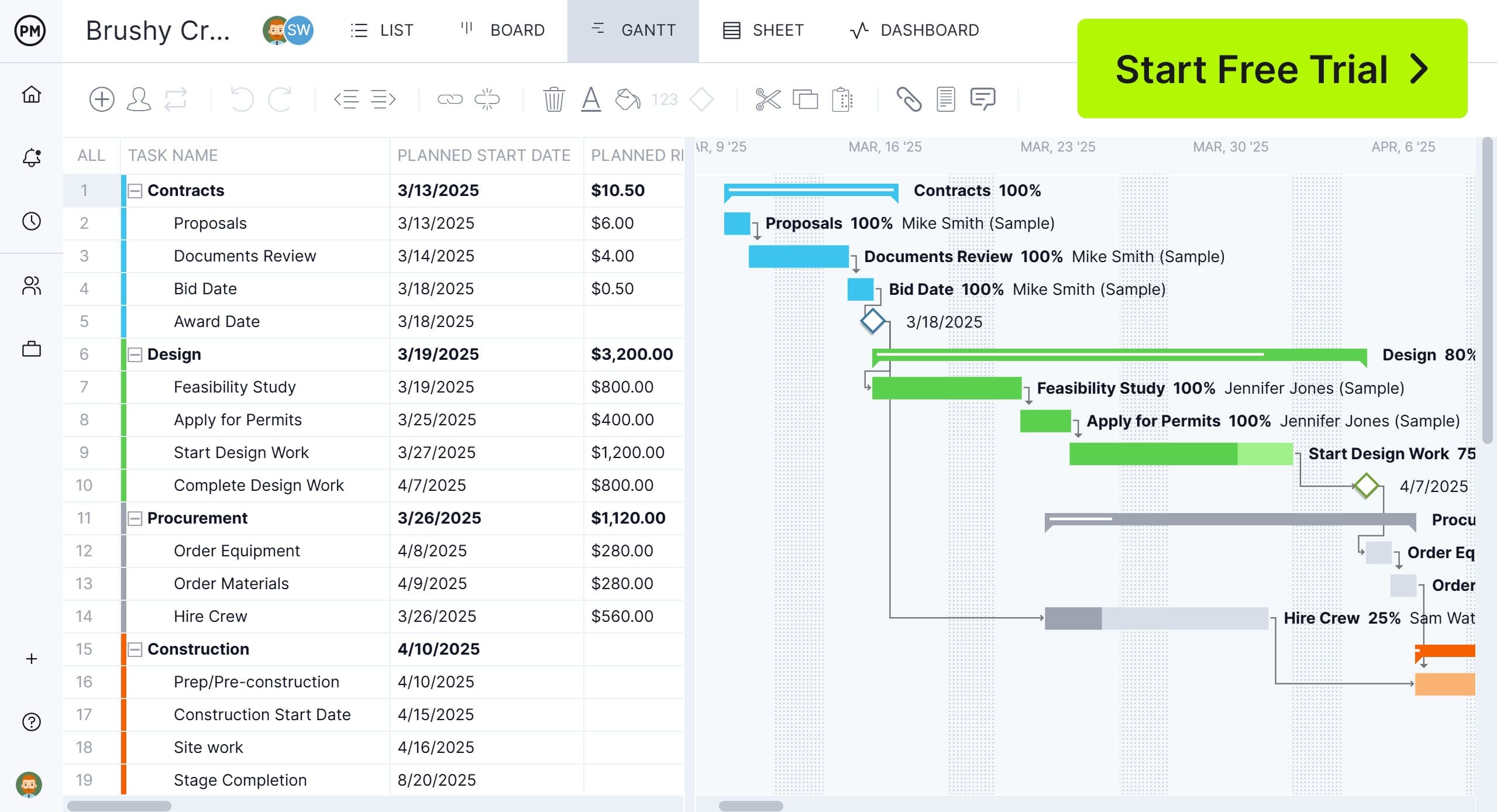
Gantt charts play a key role in production forecasting by visually mapping tasks, timelines and resource availability in a single, easy-to-understand format. They allow teams to translate forecasts into actionable production plans by scheduling tasks based on projected demand and available capacity.
ProjectManager’s Gantt chart is particularly well-suited for this because it updates in real time, automatically reflects task dependencies and lets you drag and drop to adjust timelines as forecasts change. With built-in resource tracking, workload balancing and percent-complete indicators, teams can quickly respond to shifting forecasts and stay ahead of potential bottlenecks. These features make our Gantt chart an ideal tool for turning production forecasts into efficient, trackable workflows.

Why Is Production Forecasting Important for Manufacturers?
Production forecasting is important for manufacturers because it helps them align output with actual demand, reducing both waste and missed sales opportunities. When manufacturers can accurately predict how much to produce and when, they avoid overproduction that leads to excess inventory costs and underproduction that results in stockouts or delayed deliveries.
It also supports better planning across the entire operation—from ordering raw materials and scheduling labor to managing equipment usage and shipping. Accurate forecasts lead to more efficient workflows, improved customer satisfaction and stronger profit margins. In a competitive market, the ability to forecast production needs effectively gives manufacturers a strategic advantage.
Who Participates in the Production Forecasting Process?
Production forecasting is a collaborative process that relies on input from multiple departments to ensure forecasts are accurate, realistic and aligned with overall business goals. Each team contributes unique insights that help shape a clear picture of future production needs. By working together, they create forecasts that not only meet demand but also optimize resource use and support long-term planning.
Production Manager
The production manager plays a central role by translating forecasts into actionable manufacturing schedules. They assess capacity, lead times and equipment availability to ensure the production plan is achievable and efficient. Their input helps balance output with operational constraints.
Procurement Manager
Procurement managers ensure the necessary materials are available to support the forecasted production volume. They coordinate supplier schedules, manage inventory levels and negotiate lead times to align raw material availability with production timelines.
Demand Forecaster
The demand forecaster analyzes historical sales data, market trends and customer behavior to generate accurate predictions of future demand. Their work forms the foundation of the forecast, helping the rest of the team plan around realistic expectations.
Sales and Marketing Teams
Sales and marketing teams contribute insights based on customer activity, promotional plans and upcoming product launches. Their knowledge of market shifts and customer intent helps refine the forecast and anticipate changes in demand.
Finance Team
The finance team ensures that the production forecast aligns with budget goals and profitability targets. They evaluate the cost implications of different forecast scenarios and help maintain financial discipline in production planning decisions.
Related: 12 Best Production Scheduling Software for Manufacturing Projects
What Are the Main Types of Production Forecasting Methods?
Production forecasting methods generally fall into two main categories: qualitative and quantitative. Each method has its strengths and is suited for different types of data and business situations. Manufacturers often use a combination of both to improve forecast accuracy and adaptability.
- Qualitative Forecasting Methods: These methods rely on expert judgment, experience and market knowledge rather than numerical data. They’re especially useful when historical data is limited or when forecasting for new products.
- Quantitative Forecasting Methods: These methods use mathematical models and historical data to make forecasts. They are best suited for stable environments with reliable data.
Each method has its advantages, and the right choice depends on the product type, data availability, market volatility and the level of forecast precision required. Combining qualitative insight and quantitative data often results in the most reliable production forecast.
Quantitative Production Forecasting Methods
Quantitative forecasting methods use historical data and mathematical models to predict future production output. These methods are especially useful when you have consistent, reliable data and need objective, data-driven projections. They can detect patterns, trends and seasonality in past performance to create accurate forecasts that guide manufacturing schedules, resource planning and inventory control. Below are three widely used quantitative forecasting techniques in manufacturing.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis involves collecting and analyzing data points measured at consistent time intervals, such as daily, weekly or monthly production volumes. The goal is to identify trends, seasonal effects and recurring patterns that can be projected forward. For example, if a factory consistently sees higher production output in Q4, time series analysis will highlight this seasonal spike and help forecast future Q4 production needs. This method is best suited for stable environments with recurring behavior over time.
Exponential Smoothing
Exponential smoothing is a forecasting method that applies decreasing weights to past observations, giving more importance to recent data. This allows forecasts to be more responsive to recent changes in production trends while still factoring in historical data. There are different types, including single, double and triple (Holt-Winters) exponential smoothing, which accommodate level shifts, trends and seasonality. It’s particularly useful when forecasting short-term demand or when recent changes in production patterns need to be emphasized.
Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
ARIMA is a more advanced and flexible time series forecasting model that combines autoregression (AR), differencing (I) and moving average (MA) components. It’s particularly useful for handling data that shows complex patterns, such as trends without clear seasonality. ARIMA models can adjust for non-stationary data by differencing the time series and then fitting a model that accounts for both past values and past forecast errors. It’s ideal for long-term forecasting in manufacturing environments where production data may be influenced by multiple factors and time-based dependencies.
Qualitative Production Forecasting Methods
Qualitative forecasting methods rely on expert opinions, judgment and market insights rather than historical data. These approaches are particularly useful when launching new products, entering new markets or dealing with limited or unreliable data. Instead of mathematical formulas, qualitative methods draw on the experience and knowledge of individuals or groups to anticipate future production needs. While less data-driven than quantitative methods, they provide valuable context and are often used in combination with other forecasting techniques to strengthen decision-making.
Delphi Method
The Delphi Method is a structured, interactive process where a panel of experts anonymously provides forecasts through a series of questionnaires. After each round, a facilitator summarizes the results and shares them with the group, allowing participants to revise their responses in light of the collective feedback. This process continues until a consensus is reached. The anonymity reduces the influence of dominant voices, leading to more balanced and unbiased insights. In production forecasting, it helps gather well-rounded estimates from various departments or external advisors.
Market Research
Market research involves collecting information directly from potential or current customers through surveys, interviews or focus groups. The goal is to understand demand trends, buying behaviors and preferences that could influence future production. For example, a manufacturer may survey customers about upcoming product features or price sensitivity to help gauge production volume for a new line. This method is especially valuable in new product development or when exploring unfamiliar markets, as it provides real-world data that may not be reflected in internal systems.
Related: 18 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates
Sales Force Composite
The Sales Force Composite method gathers forecasts from the sales team based on their interactions with customers and knowledge of upcoming orders or trends. Each salesperson provides their forecast for their territory, which is then aggregated and adjusted by managers to create a company-wide projection. Because salespeople are on the front lines, they often have early insight into market shifts, customer needs and competitor activity. This method is especially helpful for short-term production planning, where customer feedback and sales pipeline visibility can offer early warning signs of changes in demand.
Benefits of Production Forecasting
Production forecasting offers manufacturers a strategic advantage by helping them plan smarter, respond faster and operate more efficiently. By anticipating future demand and aligning resources accordingly, businesses can reduce risk and improve decision-making across the entire production cycle. Here are some key benefits of production forecasting.
- Improved Inventory Management: Helps avoid overstocking or stockouts by aligning production with actual demand.
- Cost Control: Reduces waste, prevents overproduction and supports more efficient use of materials and labor.
- Better Resource Allocation: Ensures the right amount of staff, equipment and materials are available when needed.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Increases on-time delivery and product availability by minimizing production delays.
- Efficient Scheduling: Allows for smoother workflow planning and reduces last-minute changes or downtime.
- Informed Decision-Making: Provides data-driven insights that support strategic planning and investment.
- Greater Agility: Helps teams respond quickly to market changes, customer demand or supply chain disruptions.
- Financial Accuracy: Improves budgeting and forecasting accuracy by aligning production plans with revenue projections.
Related Production Management Templates
Production forecasting is one method of managing production in manufacturing. While it’s best to use project management software to facilitate this process, for those not ready to upgrade, there are other tools. We have over 100 free project management templates for Excel and Word that cover all aspects of managing projects. Here are just a few to help with production management.
Production Schedule Template
Download this free production schedule template to plan, organize and track manufacturing or production activities. It outlines what needs to be produced, in what quantity, by when and by whom—often including task timelines, resource assignments and deadlines. This template helps ensure efficient workflow, minimizes downtime and keeps production on track by giving teams a clear, structured overview of daily or weekly operations.
Inventory Template
Use this free inventory template to track and manage stock levels, item details and inventory movements. It includes columns for item names, descriptions, quantities, locations and reorder status to help businesses stay organized and maintain accurate records. This tool simplifies inventory control, reduces errors and improves efficiency.
Bill of Materials Template
This free bill of materials (BOM) template is a structured document used to list all the parts, materials and components needed to manufacture a product. It typically includes item names, quantities, part numbers, descriptions and unit costs. This template helps ensure accurate production planning, cost estimation and inventory management.
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Manufacturing Projects and Processes
ProjectManager helps manage manufacturing projects and processes more effectively than templates by providing real-time data, automation and collaboration tools that static spreadsheets can’t offer. Unlike templates that require manual updates and offer limited visibility, ProjectManager’s multiple project views—like Gantt charts, kanban boards and task lists—let teams plan schedules, track tasks and monitor progress from different perspectives, making it easier to adapt to production changes, optimize resource use and ensure deadlines are met.
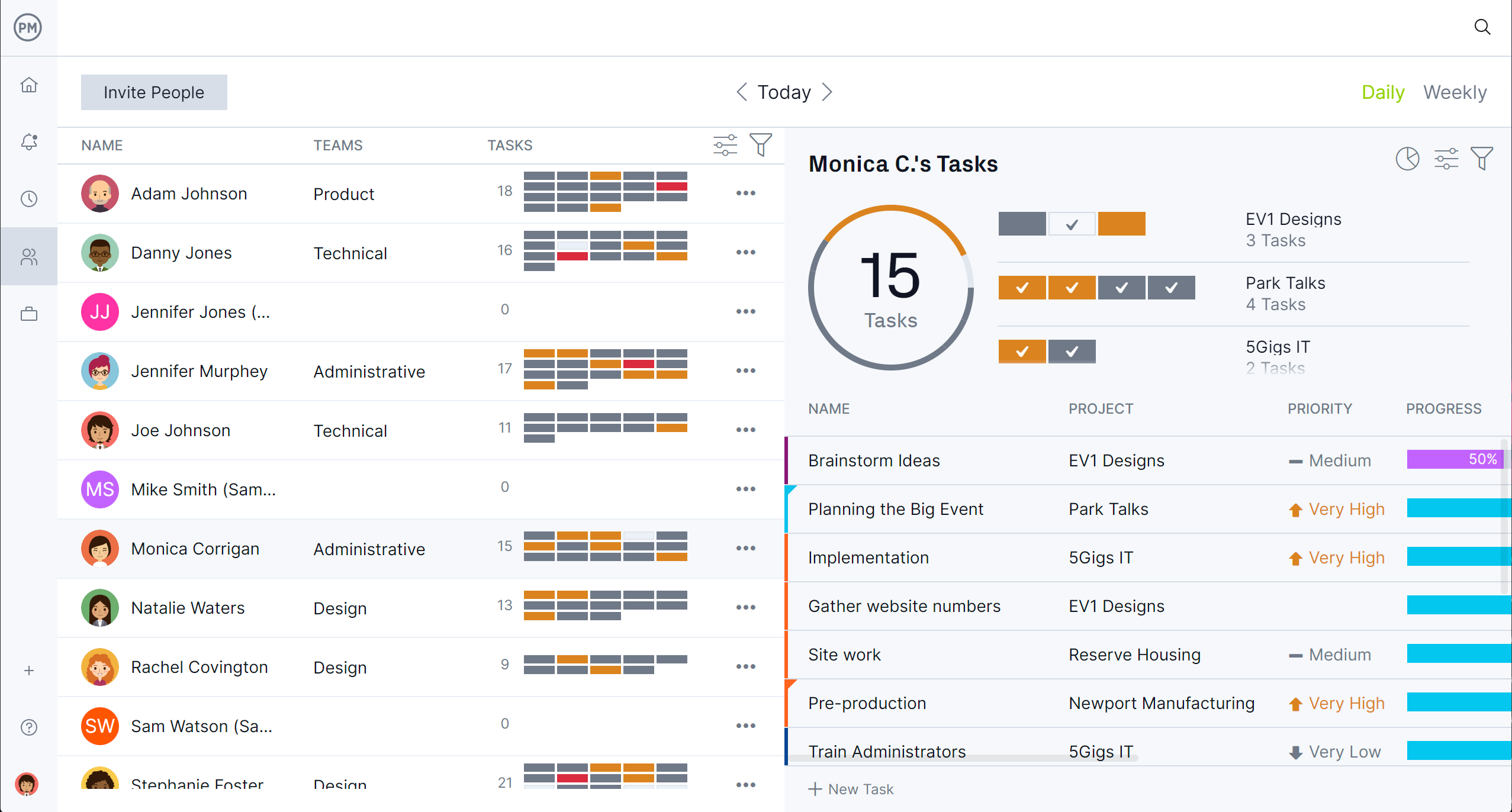
Get Visibility Into Workload, Availability and Allocation With Resource Features
Use the workload chart, availability settings and team page to help optimize productivity by giving manufacturers clear, real-time insights into team capacity and scheduling. The workload chart visually displays who is over- or under-assigned so managers can rebalance tasks to prevent burnout or idle time.
Availability settings allow for accurate planning by factoring in each team member’s work hours, shifts and time off. The team page centralizes this information, making it easy to view roles, assignments and workloads at a glance, which supports efficient resource allocation and smooth production workflows.

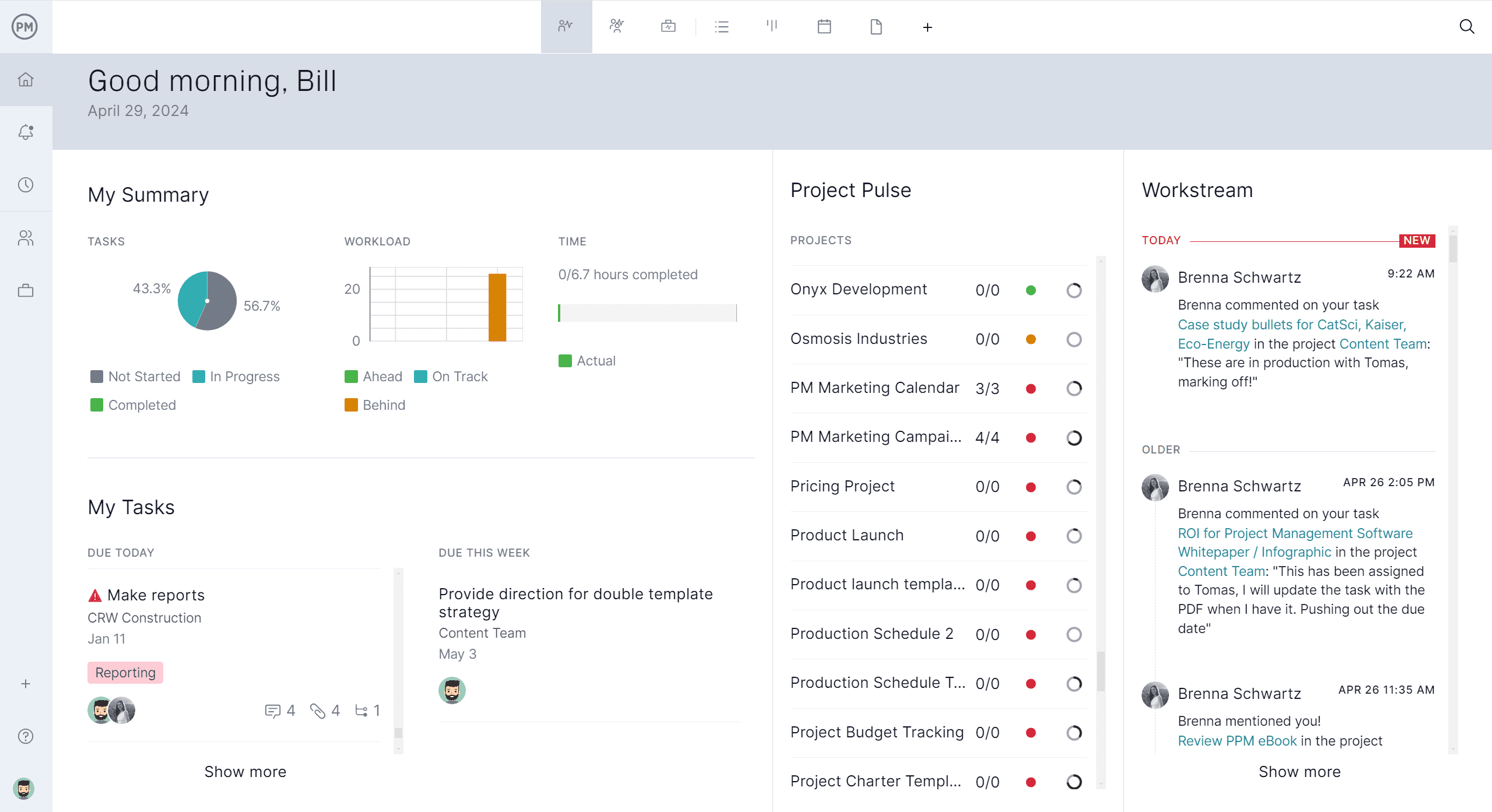
Track Costs, Resources and More With Real-Time Project Dashboards, Reports and Timesheets
Tracking tools, such as dashboards, reports and timesheets, work together to streamline manufacturing project and process management by providing real-time visibility into every aspect of production. Tracking tools monitor task progress, resource use and dependencies so managers can quickly spot issues and make adjustments.
Live dashboards display key metrics like output, efficiency and deadlines to keep teams aligned. Customizable reports offer detailed insights into performance, costs and resource allocation while secure timesheets log labor hours to ensure accurate payroll and cost tracking. Together, these tools support better planning, faster decision-making and more efficient operations.

Related Production Content
Production forecasting is part of the larger project management process. For those who care to learn more about this discipline, check out the links below. There are articles on scheduling, reporting and much more.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.