Production engineering sits at the intersection of design, manufacturing and continuous improvement, shaping how products are built at scale. For manufacturers, production engineering influences efficiency, quality and cost control across operations. This guide explores how production engineering supports modern factories, connects processes with technology and helps organizations respond faster to changing demand and competitive pressure in global industrial environments worldwide.
What Is Production Engineering?
Production engineering is a discipline focused on designing, optimizing and managing manufacturing processes to produce goods efficiently and consistently. It bridges product design and factory operations by defining workflows, selecting equipment, standardizing methods and integrating technology. The goal is to ensure products can be manufactured at required quality levels, volumes and costs while supporting safety, reliability and continuous improvement initiatives.
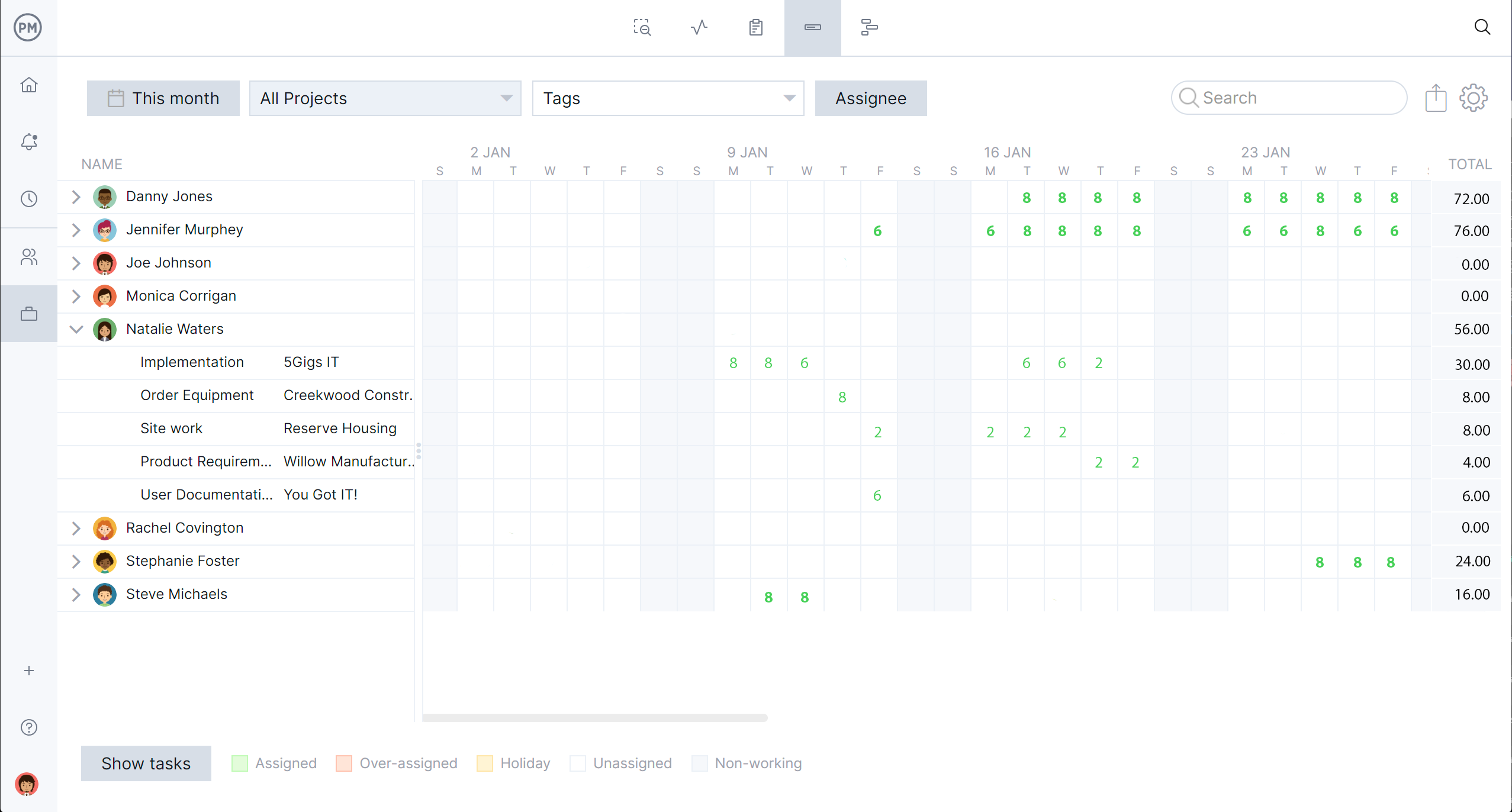
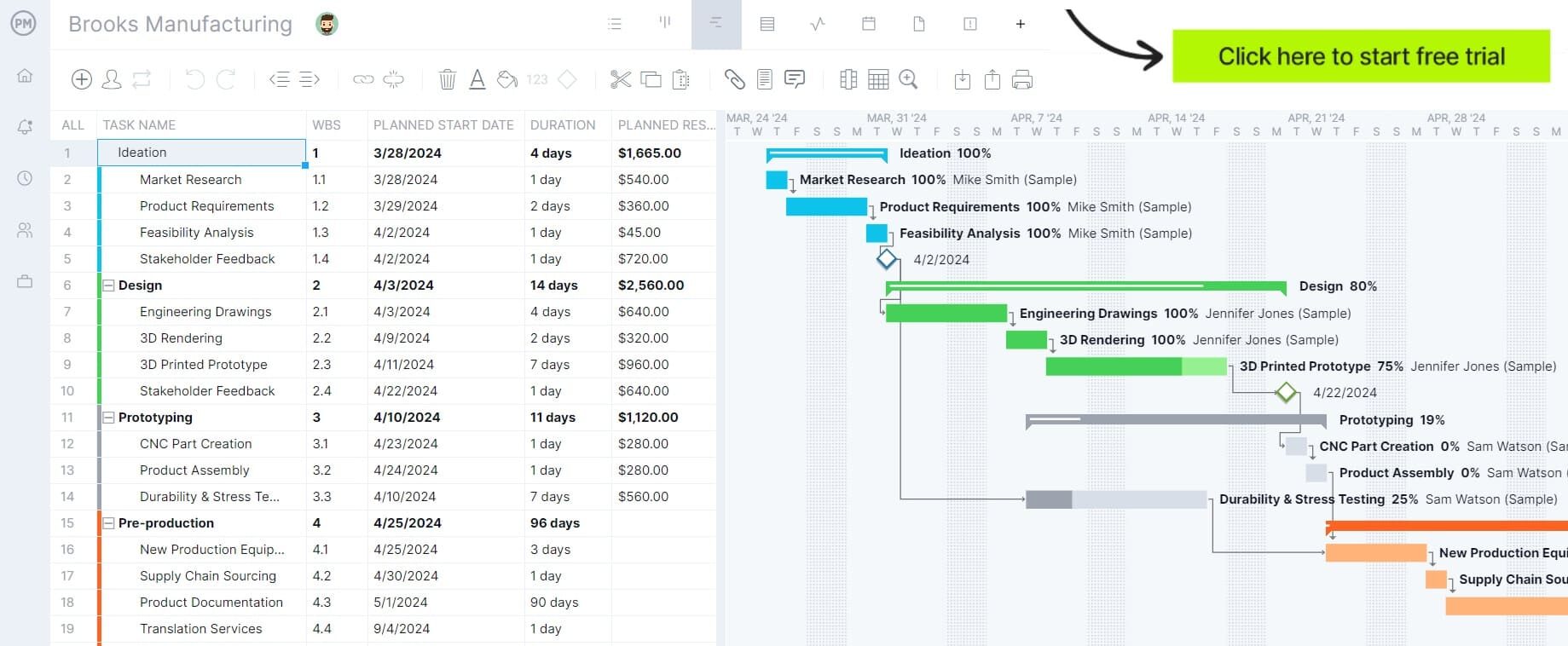
ProjectManager supports production engineering by helping teams plan, coordinate and optimize how work is designed, sequenced and executed. Gantt charts help plan and visualize production sequences, identify bottlenecks in workflows and coordinate engineering tasks with production phases. Built-in resource management is also helpful for assigning people, machines, tools and materials to specific tasks to balance workloads and keep production running smoothly.

Production Engineering Objectives
Production engineering objectives focus on improving manufacturing performance for the business. They aim to increase efficiency, reduce waste, control costs, ensure consistent quality, improve safety and enable scalable production systems that support demand growth, faster throughput and long-term operational competitiveness.
Improve Production Efficiency and Throughput Rates
Manufacturing businesses use production engineering to analyze workflows, balance production lines and remove bottlenecks. By standardizing processes, optimizing layouts and applying time and motion studies, production engineering increases output rates while reducing idle time, delays and unnecessary movement across manufacturing operations and production stages.
Reduce Manufacturing Costs and Process Waste
Through production engineering, manufacturers identify inefficiencies that drive excess cost and waste. Techniques such as process mapping, root cause analysis and continuous improvement help reduce scrap, rework and overprocessing. Optimized material flows and standardized methods lower operating costs while improving overall process efficiency and resource utilization.
Ensure Consistent Product Quality and Process Stability
Production engineering establishes controlled processes that support consistent product quality. By defining standards, tolerances and inspection methods, manufacturers reduce variation and defects. Stable workflows, documented procedures and data-driven monitoring help maintain repeatable outcomes while ensuring products meet specifications across production runs and operating conditions.
Related: 23 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates
Optimize Labor, Material and Equipment Utilization
Manufacturers rely on production engineering to align labor, materials and equipment with production demand. Capacity planning, workload balancing and equipment optimization reduce underutilization and downtime. This coordinated approach ensures resources are used efficiently, supporting productivity goals while preventing overstaffing, material shortages or equipment bottlenecks.
Enable Scalable and Repeatable Manufacturing Operations
Production engineering creates manufacturing systems that can scale without sacrificing performance. Standardized processes, modular layouts and documented workflows allow operations to expand or adapt consistently. This repeatability supports higher volumes, new product introductions and multi-site manufacturing while maintaining efficiency, quality and operational control.

Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template to manage your projects better.
Production Engineering Processes
A production engineering process refers to the structured set of methods used to design, manage and improve manufacturing operations. These processes define how materials, labor and equipment are organized, controlled and optimized to ensure products are produced efficiently, consistently and at scale while meeting quality, cost and performance objectives.
Manufacturing Process Design and Optimization
Manufacturing process design and optimization focuses on defining how products are made from start to finish. Production engineers select workflows, equipment and layouts that minimize waste and maximize efficiency. Ongoing analysis and adjustments help improve cycle times, reduce bottlenecks and adapt processes to changing production requirements.
Production Line Balancing and Takt Time Analysis
Production line balancing and takt time analysis align workstations with customer demand. Production engineering distributes tasks evenly across the line to prevent overloads or idle time. Takt time establishes production pace, helping manufacturers synchronize operations, stabilize output and maintain predictable throughput across manufacturing systems.
Quality Assurance Systems and In-Process Controls
Quality assurance systems and in-process controls are used to maintain consistent product standards during production. Production engineering defines inspection points, control limits and monitoring methods. These controls detect defects early, reduce rework and ensure processes remain stable while meeting design specifications and regulatory requirements.
Standardization of Operating Procedures
Standardization of operating procedures ensures manufacturing tasks are performed consistently across shifts and teams. Production engineering documents best practices, work instructions and safety requirements. Clear standards reduce variability, improve training efficiency and support repeatable results, even as production volumes or staffing levels change.
Continuous Process Improvement Cycles
Continuous process improvement cycles focus on systematically enhancing manufacturing performance over time. Production engineering applies feedback, data analysis and improvement methodologies to refine processes. Regular evaluation helps eliminate inefficiencies, adapt to new constraints and drive incremental gains in productivity, quality and operational reliability.
Production Engineering Methods
A production engineering method is a structured technique used to analyze, design or improve manufacturing operations. These methods provide systematic ways to identify inefficiencies, control variation and optimize performance. Manufacturing businesses apply production engineering methods to improve decision-making, stabilize processes and achieve measurable gains in efficiency, quality, cost control and operational reliability across production systems.
Value Stream Mapping for Material and Information Flow
Value stream mapping is used to visualize how materials and information move through a manufacturing process. Production engineering applies this method to identify waste, delays and handoff issues. Mapping current and future states helps manufacturers streamline flow, reduce lead times and improve coordination between production stages.
Theory of Constraints and Bottleneck Management
The theory of constraints focuses on identifying and managing the weakest point in a production system. Production engineering uses this method to prioritize improvements where constraints limit throughput. By elevating bottlenecks and aligning resources, manufacturers increase output without unnecessary investment across non-constraining processes.


Statistical Process Control and Control Charts
Statistical process control uses data and control charts to monitor process behavior over time. Production engineering applies this method to detect variation, prevent defects and maintain stability. Continuous monitoring allows manufacturers to address issues early, ensuring consistent quality and predictable manufacturing performance.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure mode and effects analysis evaluates potential process failures before they occur. Production engineering uses FMEA to assess risk, prioritize preventive actions and improve reliability. By identifying failure causes and impacts, manufacturers reduce downtime, defects and safety incidents across production operations.
Lean Manufacturing Systems and Waste Elimination
Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-adding activities from production processes. Production engineering applies lean principles to reduce waste related to motion, inventory, overproduction and waiting. Streamlined workflows improve efficiency, lower costs and enhance responsiveness to customer demand.
Six Sigma DMAIC Methodology
Six Sigma DMAIC provides a data-driven framework for process improvement. Production engineering uses define, measure, analyze, improve and control phases to reduce variation and defects. This method supports disciplined problem-solving, delivering measurable improvements in quality, consistency and overall manufacturing performance.
Production Engineering Tools & Technology
Tools and technology play a central role in production engineering by turning process design into executable, measurable operations. Software systems, automation and digital platforms allow manufacturers to plan, control and optimize production activities. These technologies support data-driven decisions, real-time visibility and continuous improvement across modern manufacturing environments.
Production Planning and Scheduling Software
Production planning and scheduling software is used to plan manufacturing activities, allocate resources and sequence production orders. These tools help production engineers align demand with capacity, manage constraints and monitor progress, ensuring materials, labor and equipment are available when needed.
- ProjectManager
- SAP PP (Production Planning)
- Oracle Manufacturing Cloud
- Siemens Opcenter APS
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- Asprova APS
Related: 10 Best Production Planning Software
Manufacturing Automation, Robotics and PLC Systems
Automation, robotics and PLC systems control and execute physical manufacturing processes with minimal manual intervention. Production engineering uses these technologies to improve precision, speed and safety. They enable consistent execution of tasks, reduce human error and support high-volume, repeatable production environments.
- Siemens SIMATIC PLC Systems
- Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley PLCs
- FANUC Industrial Robots
- ABB Robotics Systems
- Omron Automation Controllers
CAD, CAM and Digital Manufacturing Systems
CAD, CAM and digital manufacturing systems support product design and manufacturing integration. Production engineering uses these tools to translate designs into production-ready instructions. They improve accuracy, reduce rework and enable faster transitions from engineering design to shop-floor execution.
- AutoCAD
- SolidWorks
- Siemens NX
- Mastercam
- CATIA
Quality Inspection Systems and Metrology Tools
Quality inspection systems and metrology tools are used to measure, inspect and verify product specifications during manufacturing. Production engineering relies on these tools to detect defects, control variation and ensure components meet dimensional, functional and regulatory requirements throughout production and final inspection stages.
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)
- Zeiss Industrial Metrology Systems
- Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence Solutions
- Keyence Vision Inspection Systems
- Mitutoyo Precision Measuring Instruments
Industrial Internet of Things and Manufacturing Data Analytics
Industrial Internet of Things and manufacturing data analytics tools collect, analyze and visualize real-time production data. Production engineering uses these technologies to monitor equipment performance, identify trends and support predictive decision-making that improves efficiency, reliability and overall manufacturing system performance.
- Siemens MindSphere
- PTC ThingWorx
- Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk
- GE Digital Predix
- IBM Maximo Application Suite
Production Engineering Roles
We’ve gone over the most important production engineering tools and methods, but none of these can be successfully applied without people. Let’s now shift our focus to the human resources that make production engineering possible.
- Production Engineer Responsibilities and Scope: Oversees manufacturing processes from design to execution, ensuring efficiency, quality and cost targets are met while coordinating production workflows, equipment selection, documentation and continuous improvement initiatives across operations.
- Process Engineer and Process Optimization Role: Focuses on analyzing, designing and improving manufacturing processes to reduce waste, increase throughput and stabilize output by applying data analysis, standardization and optimization techniques throughout production systems.
- Industrial Engineer in Production Systems Design: Designs efficient production systems by optimizing layouts, workflows and resource utilization, balancing labor, materials and equipment to improve productivity, ergonomics, safety and overall manufacturing performance.
- Operations Engineer in Manufacturing Execution: Manages day-to-day execution of manufacturing operations, coordinating schedules, resources and equipment while resolving operational issues to maintain consistent output, meet delivery commitments and support production targets.
- Quality Engineer and Process Compliance Oversight: Ensures manufacturing processes comply with quality standards and regulations by implementing inspections, controls and corrective actions to reduce defects, maintain consistency and support continuous compliance improvement.
Free Production Management Templates
We’ve created dozens of free templates for Excel, Word and Google Sheets that can help manufacturers manage their daily operations.
Production Schedule Template
This production schedule template helps plan tasks, sequence activities and allocate resources, providing clear visibility into timelines, inventory and capacity to support consistent manufacturing output.
Daily Production Report
This daily production report captures output, downtime and issues, giving managers insight into performance, variances and corrective actions needed to keep operations aligned with targets.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Template
An SOP template documents standardized procedures, roles and controls, ensuring tasks are performed consistently, safely and efficiently while supporting training, compliance and repeatable production results.
How ProjectManager Helps with Production Management
From Gantt charts to task lists and more, ProjectManager has built-in tools that improve production management. By uniting planning, execution and measurement tools, ProjectManager helps engineering teams plan workflows with clarity, use data to spot inefficiencies, track real performance against plans and much more.
Real-time Resource Management
It’s easy to assign people, tools and machines to specific tasks in ProjectManager. Use our built-in tools to help balance workloads across teams and equipment. This ensures capacity planning keeps production running efficiently. Timesheets can also capture actual time spent on tasks to track engineering and production labor costs.
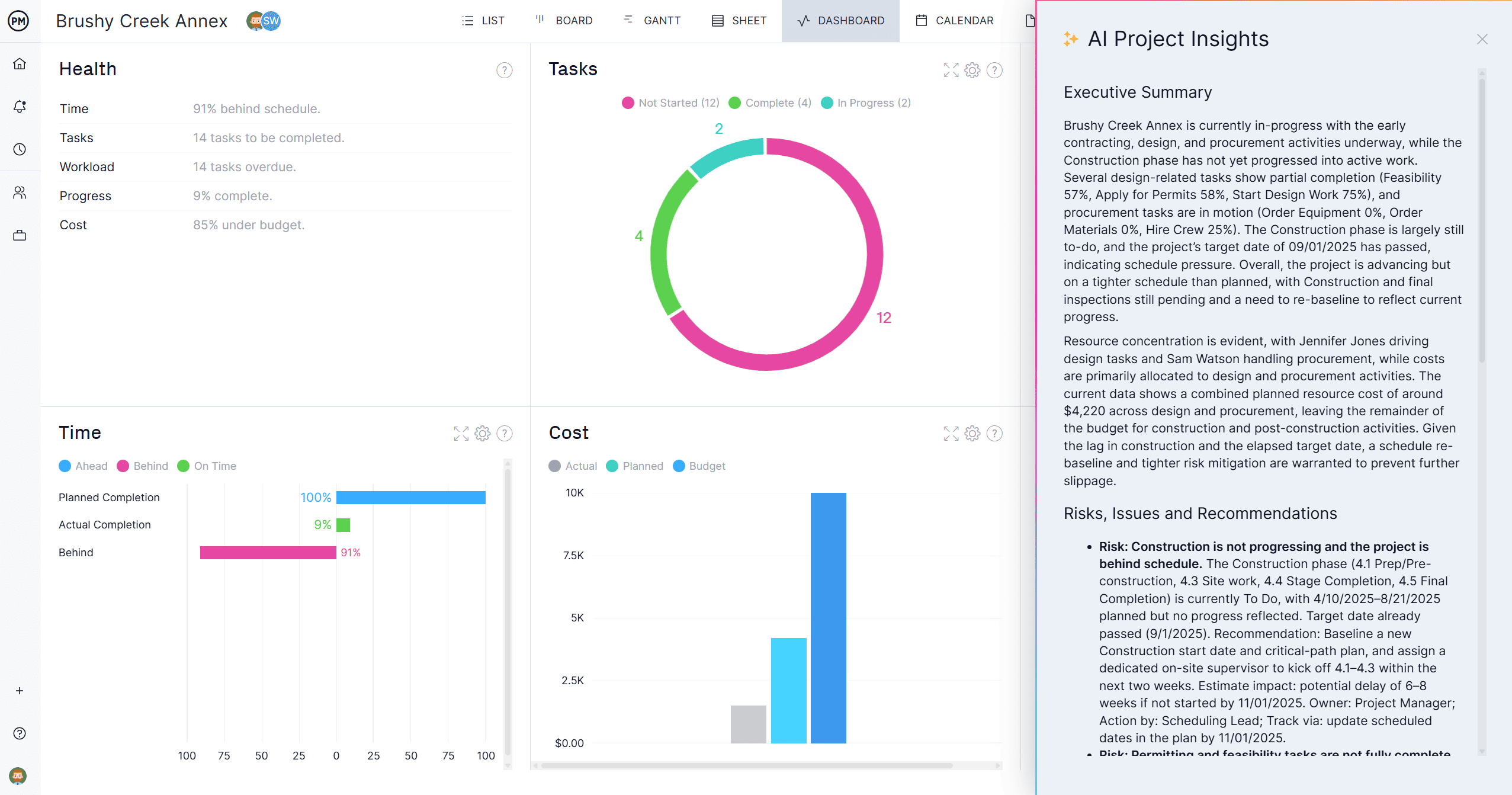
Use AI Technology to Improve Reports
In just one click, AI Project Insights analyzes your project data and makes tailored recommendations. It can help spot risks in the project timeline, provide suggestions on how to reallocate resources or flag critical path tasks that need your attention. Use the information from AI Project Insights to create tailored reports to share with project stakeholders.
Related Production Management Content
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office, on the job site or anywhere else. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.