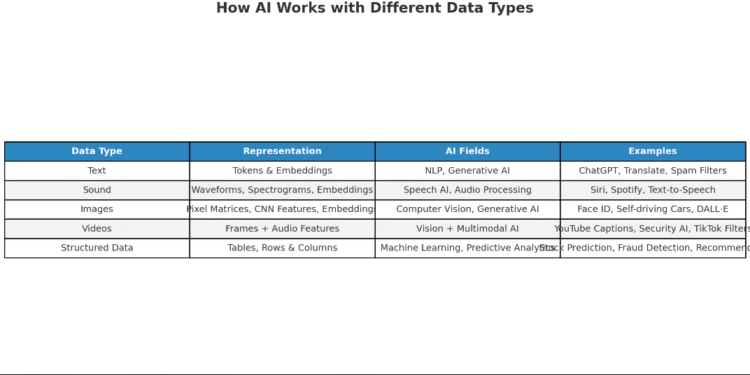
Artificial Intelligence (AI) thrives on data. Just like humans use senses to see, hear, and read, machines also process information from different types of data: text, sound, images, videos, and more. Each type requires special techniques to represent, transform, and understand it. Let’s explore how AI works with different data types, the tools used, and which AI fields are applied.
Representation:-
Tokenization: Text is broken down into smaller pieces (tokens) such as words or subwords.
Embeddings: Each token is mapped into a vector (numerical representation) that captures meaning and relationships between words.
Language Models: Transformers like GPT or BERT process these embeddings to understand and generate human-like text.
AI Fields Involved
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Generative AI (for chatbots, story generation, summarization)
Examples
ChatGPT answering questions
Google Translate converting one language to another
Email spam detection
Representation:-
Waveforms: Raw audio signals captured as time-series data.
Spectrograms: Converting sound into 2D visual frequency maps.
Embeddings: Audio embeddings represent characteristics like pitch, rhythm, and tone in vector space.
Processing Methods:-
Feature extraction (MFCCs, spectrograms) for speech recognition.
Embedding models for sound similarity and music recommendation.
Generative Models for text-to-speech or music generation.
AI Fields Involved:-
Speech Recognition (ASR)
Audio Signal Processing
Generative AI for Audio
Examples:-
Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant understanding voice commands
Spotify recommending songs based on audio similarity
Text-to-speech systems like ElevenLabs
Pixels & Matrices: An image is stored as a grid (matrix) of pixel values.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) extract features like edges, textures, and objects.
Embeddings: Represent images in vector form for similarity search (e.g., Google Images).
Processing Methods:-
Object Detection (YOLO, Faster R-CNN)
Image Classification (ResNet, VGG)
Generative Models (GANs, Diffusion Models for image creation)
AI Fields Involved:-
Computer Vision
Generative AI for Images
Examples:-
Face recognition on smartphones
Self-driving cars detecting pedestrians and signs
AI art tools like DALL·E and MidJourney
Representation:-
Combination of image sequences + audio.
Processed as frames over time (spatio-temporal data).
Embeddings combine both vision and sound features.
AI Fields Involved:-
Computer Vision (action recognition, video summarization)
Multimodal AI (connecting text, audio, video together)
Examples
YouTube auto-captioning
Security cameras detecting suspicious activity
TikTok filters powered by real-time vision AI
Representation:-
Stored in tables, rows, and columns.
Used with statistical models, regression, and ML algorithms.
AI Fields Involved:-
Machine Learning (ML)
Predictive Analytics
Examples:-
Predicting stock prices from financial data
Recommendation systems on Amazon
Fraud detection in banking
AI adapts to different data types by representing them in mathematical forms that machines can understand — text as tokens, sound as spectrograms, images as pixel matrices, and numbers as structured datasets. Depending on the data type, we use different fields of AI:
Text → NLP & Generative AI
Sound → Speech AI & Audio Generative AI
Images → Computer Vision & Generative Vision Models
Videos → Multimodal AI
Structured Data → Machine Learning
Together, these methods make it possible for AI to read, listen, see, and even create — pushing technology closer to human intelligence.