Whether a professional project manager or an accidental project manager who suddenly finds a project assigned to them, knowing how to manage a project is essential. You can never know enough for the journeymen and newbies should try to wing it.
Let’s break down the process of how to manage a project step by step. Below are the 10 pieces that show how to manage a project successfully. While we recommend using project management software, for those not ready to upgrade, we end with free templates.
1. Define the Project Goals and Objectives
Defining clear goals and objectives is the foundation of how to manage a project successfully. This step ensures all stakeholders have a shared understanding of what the project aims to achieve and provides a roadmap for decision-making, planning and execution.
Start by identifying the project purpose. Use SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound) goals and know the difference between goals and objectives (the former are broad, high-level outcomes the project aims to achieve, while the latter are specific, actionable steps to achieve the goals).
Be sure to engage clients, team members and executives to ensure the goals are aligned with stakeholder expectations and business needs. Record the goals in a project charter or scope statement and share them with the team to ensure clarity, accountability and commitment. This provides a clear benchmark for measuring success, minimizes scope creep and helps to prioritize tasks and resource allocation when scheduling work on a Gantt chart.
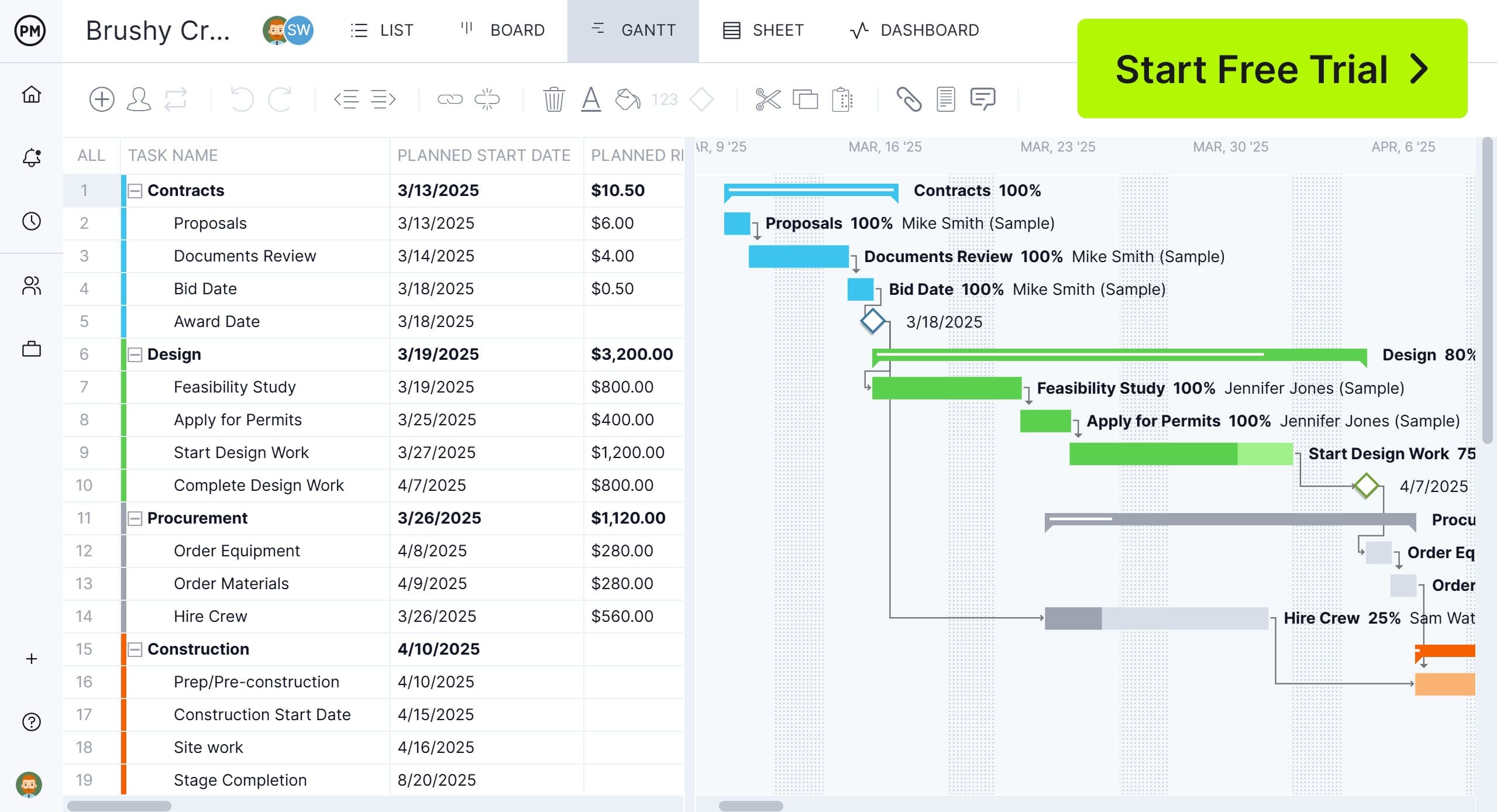
Gantt charts are usually part of project management software, which adds efficiency to the project management process. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with robust Gantt charts that schedule tasks, resources and costs.
They can also link all four types of task dependencies to avoid cost overruns, filter for the critical path and set a baseline to track planned effort against actual effort in real time to help projects stay on track. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

2. Identify Project Stakeholders and Make a Plan to Engage Them
Since we’ve mentioned stakeholders, let’s define what they are. Stakeholders are individuals, groups or organizations that have an interest in or are affected by the project. Identifying them early and planning how to engage them ensures strong communication, collaboration and project success.
Stakeholders can be internal, such as the project sponsor, team members, senior management and other departments, or external, such as clients or customers, vendors and suppliers, regulatory bodies and investors or partners. These are first identified and then categorized by the amount of influence and interest they have in the project.
The next part of how to manage a project is developing a stakeholder engagement plan. This includes the communication method they prefer (meetings, progress reports, emails, etc.), who the responsible person is that gets that missive and the frequency of the communication.
Be sure to manage stakeholder expectations by being clear about the project scope, deliverables and timetables. Address concerns proactively to maintain trust and stay flexible and adjust engagement strategies based on stakeholder feedback. This ensures alignment, reduces conflicts and misunderstandings, improves decision making and gets buy-in and support.
3. Make a Work Breakdown Structure to Define the Project Scope
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a key tool in project management that helps define and organize the project’s scope by breaking it down into smaller, manageable components. It ensures clarity, accountability and effective planning by identifying all essential tasks, deliverables, milestones and dependencies.
By using a WBS, project managers can visualize the entire project, allocate resources effectively and set realistic deadlines, which is important when figuring out how to manage a project. It prevents scope creep and ensures all project elements align with the defined objectives.
- Project Tasks: Specific actions or work packages that must be completed to achieve project goals. Tasks should be clearly defined, assigned and measurable.
- Project Deliverables: The tangible or intangible outputs that result from completing tasks. Deliverables should align with project goals and stakeholder expectations.
- Project Milestones: These are major checkpoints that indicate progress in the project life cycle. Milestones help track whether the project is on schedule.
- Task Dependencies: The relationship between tasks, where one task depends on another before it can start or finish. Identifying dependencies ensures a logical workflow and prevents bottlenecks.
4. Make a Project Schedule
A project schedule is a detailed timeline that outlines all project activities, tasks, milestones and deadlines. It serves as a roadmap to ensure the project is completed on time and within scope, helping teams stay on track and efficiently manage resources.
When it comes to how to manage a project, the schedule is critical. It includes task assignments, estimated durations, task dependencies, milestones and resource allocation. This keeps projects organized and on track, identifies potential delays and risks early, allocates resources efficiently and improves team coordination.
Below are some methods and tools to help make the schedule.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks to determine the shortest project duration. Helps prioritize critical tasks to avoid project delays.
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT): Uses optimistic, pessimistic and most likely time estimates to calculate task durations. Useful for projects with high uncertainty in task completion times.
- Project Network Diagrams: A visual representation of project tasks and their dependencies. Helps identify bottlenecks and task sequencing for smooth execution.
- Gantt Charts: A bar chart that visually maps tasks over a timeline. Shows task start and end dates, dependencies and progress. Widely used for tracking deadlines and resource allocation.
5. Define the Project Resource Requirements
Project resource requirements refer to the people, materials, equipment, budget and technology needed to complete a project successfully. Identifying and allocating these resources ensures that the project progresses smoothly, stays on schedule and remains within budget.
This ensures efficient resource utilization and prevents shortages. It also helps control project costs and avoid budget overruns. Identifying, allocating and managing resources improves task execution, workflow efficiency and reduces risks associated with delays and misallocation.
6. Estimate Costs and Make a Project Budget
Cost estimation involves predicting the total expenses required to complete a project, while a project budget is a financial plan that outlines all expected costs, resource allocations and financial constraints. A well-planned budget ensures cost control, financial efficiency and project feasibility.
How to manage a project includes identifying cost categories: direct costs, which are expenses directly tied to project execution and indirect costs, which are overhead costs that support the project. There are also contingency costs that are a buffer for unforeseen risks or changes.
Several cost estimating methods can be used, from analogous (uses past project data) to parametric (applies statistical formulas based on project size and complexity) and bottom-up (breaks down tasks into individual costs and sums them up) to three-point (uses optimistic, pessimistic and most likely cost estimates for accuracy).
Next, develop a budget by organizing estimated costs into a structured budget plan. Make sure that there is financial alignment with the project goals and funding availability. Distribute budgeted funds across different phases of the project life cycle and set aside a contingency reserve for unexpected expenses. Budgets must be monitored and expenses tracked throughout the project’s life cycle.
7. Identify Potential Project Risks and Define Mitigation Strategies
Project risk management involves identifying, analyzing and addressing potential risks that could impact the project’s success. Risks can arise from budget constraints, resource shortages, technology failures, stakeholder conflicts or external factors like regulatory changes. A proactive approach to risk management helps ensure smooth project execution and minimizes disruptions.
Once risks are identified by conducting a brainstorming session, reviewing historical data and using a risk breakdown structure, they must be analyzed and prioritized. This is based on the likelihood of the risk occurring and its impact on the project. A risk matrix helps to classify risks as low, moderate, high or crucial. A mitigation strategy to determine whether risks should be eliminated, reduced, transferred or accepted will also be created.
Risk identification and mitigation are critical to how to manage a project. They prevent delays and costly setbacks. This also leads to improving decision-making with proactive risk planning. Stakeholder confidence is enhanced, which supports project success. Finally, it ensures smooth execution by reducing uncertainties.
8. Procure Project Resources from Vendors
Project procurement involves identifying, selecting and managing external vendors or suppliers to obtain the necessary resources, such as materials, equipment or services, needed to complete a project. A well-planned procurement process ensures quality, timely delivery and cost-effectiveness while minimizing risks.
This begins by defining procurement needs, researching and identifying potential vendors. Then, request quotes and proposals, negotiate contracts and terms and issue purchase orders. After this, how to manage a project requires the close monitoring of vendor performance and deliveries to ensure all is going as planned.
9. Assemble a Project Team and Begin Project Execution
Assembling a project team involves identifying, selecting and assigning roles to individuals with the skills and expertise needed to complete the project successfully. A well-structured team ensures efficient collaboration, accountability and smooth project execution.
To assemble a project team, first define the project roles and responsibilities by using a RACI matrix to determine who is responsible, accountable, consulted and informed for each task. Also, assign roles based on skills, experience and project needs.
Then select and onboard team members. Explain the project details, goals and expectations and provide them with the necessary tools, resources and training. Set up regular meetings and establish the collaborative process.
Once the team is in place, project execution begins—this is the phase where the project plan is put into action and tasks are carried out to achieve project objectives.
10. Use a Project Tracking Software to Monitor Project Execution
Project tracking is the ongoing process of monitoring progress, identifying risks and ensuring the project stays on schedule, within budget and meets quality standards. Using project tracking software helps teams stay organized, accountable and adaptable throughout execution.
When looking for project tracking software, use one with real-time visibility into the project progress. This allows project managers to identify risks easily and adjust plans proactively. It also improves team accountability and communication, keeps projects on track, within budget and aligned with goals.
Free Project Management Templates
For those who are not ready to upgrade to project tracking software or project management with a full suite of features to plan, manage and track projects, there are workarounds. These free templates, a few of the over 100 project management templates for Excel and Word on our site, can help with figuring out how to manage a project.
Project Plan Template
Download this free project plan template for Word to organize, track and document all the key elements required for a successful project. It serves as a guide throughout the project life cycle, outlining all tasks, timelines, resources, risks and deliverables.
Project Budget Template
Use this free project budget template for Excel to plan and track all the financial aspects of a project. It helps project managers allocate resources, set financial goals and monitor expenditures throughout the project lifecycle.
Project Dashboard Template
A project dashboard is a visual tool used to track and display key project metrics, progress and performance at a glance. This free project dashboard template for Excel consolidates important project data into a single view, making it easier for project managers, stakeholders and teams to monitor the project’s health.
How to Manage a Project With ProjectManager
As mentioned above, it’s not recommended to manage a project with templates. They are a cheap alternative, but one gets what they pay for. Templates are fine for some things, but managing dynamic projects with static documents is not one of them. Project management software is designed to work more efficiently.
ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that plans and schedules projects with multiple views. We’ve already mentioned our powerful Gantt charts, but teams can choose between kanban boards and task lists to execute their tasks, while stakeholders can get a monthly overview of the project on the calendar view.
Allocate Resources and Monitor Their Utilization
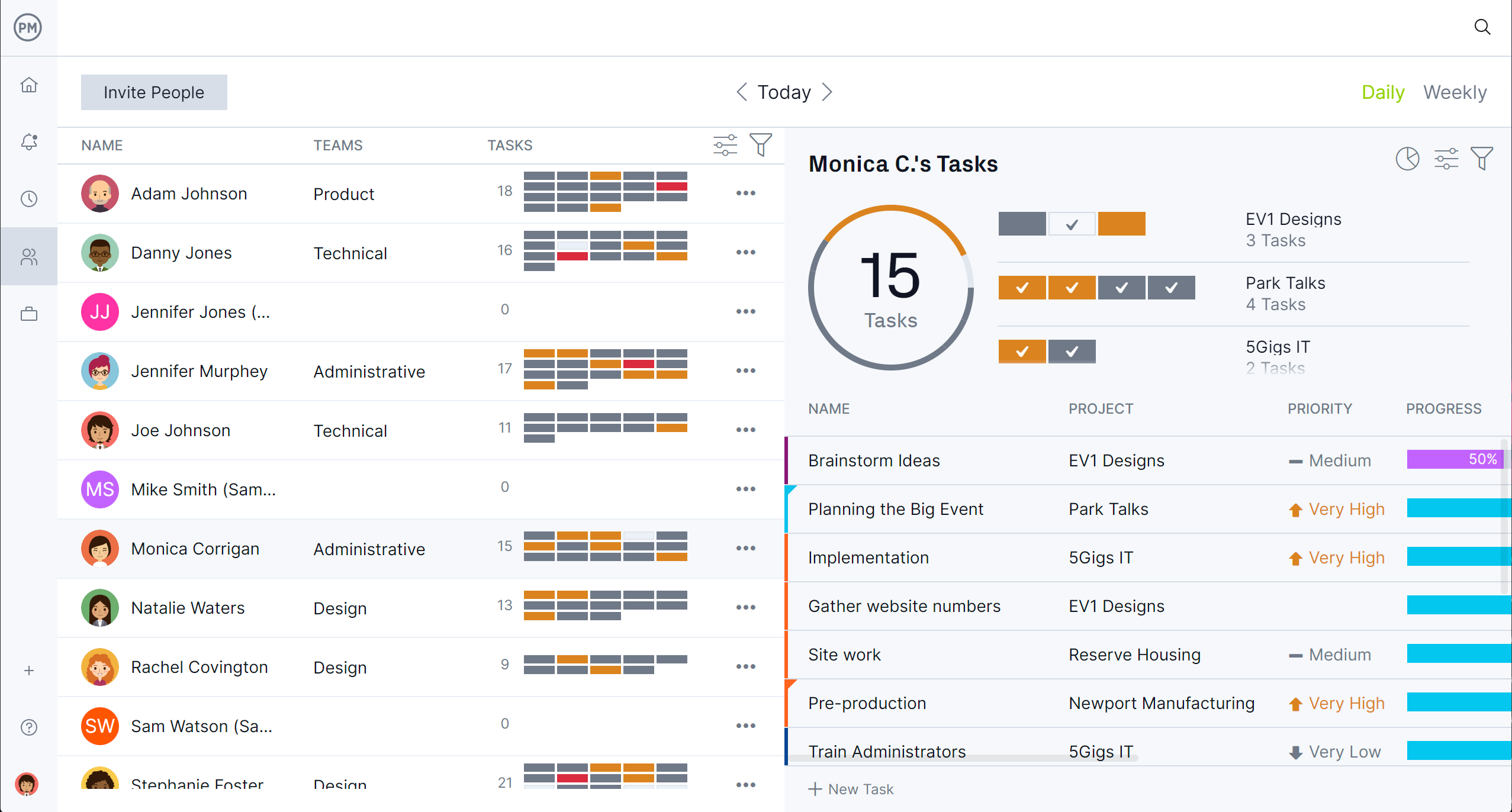
Human and nonhuman resources are scheduled on the Gantt chart, but before assigning tasks to teams, set their availability when onboarding. This shows who has PTO, vacation or when global holidays occur. It also lists skills and pay rate, all of which streamline the assignment process. To view resource allocation across one or multiple projects, use the color-coded workload chart. It makes seeing who is overallocated or underutilized quick and easy.
Then, balance the team’s workload to keep everyone working at capacity without leaving the chart. There’s also a team page that shows daily or weekly activities. It can be filtered by progress or priority and tasks can also be updated without leaving the page.

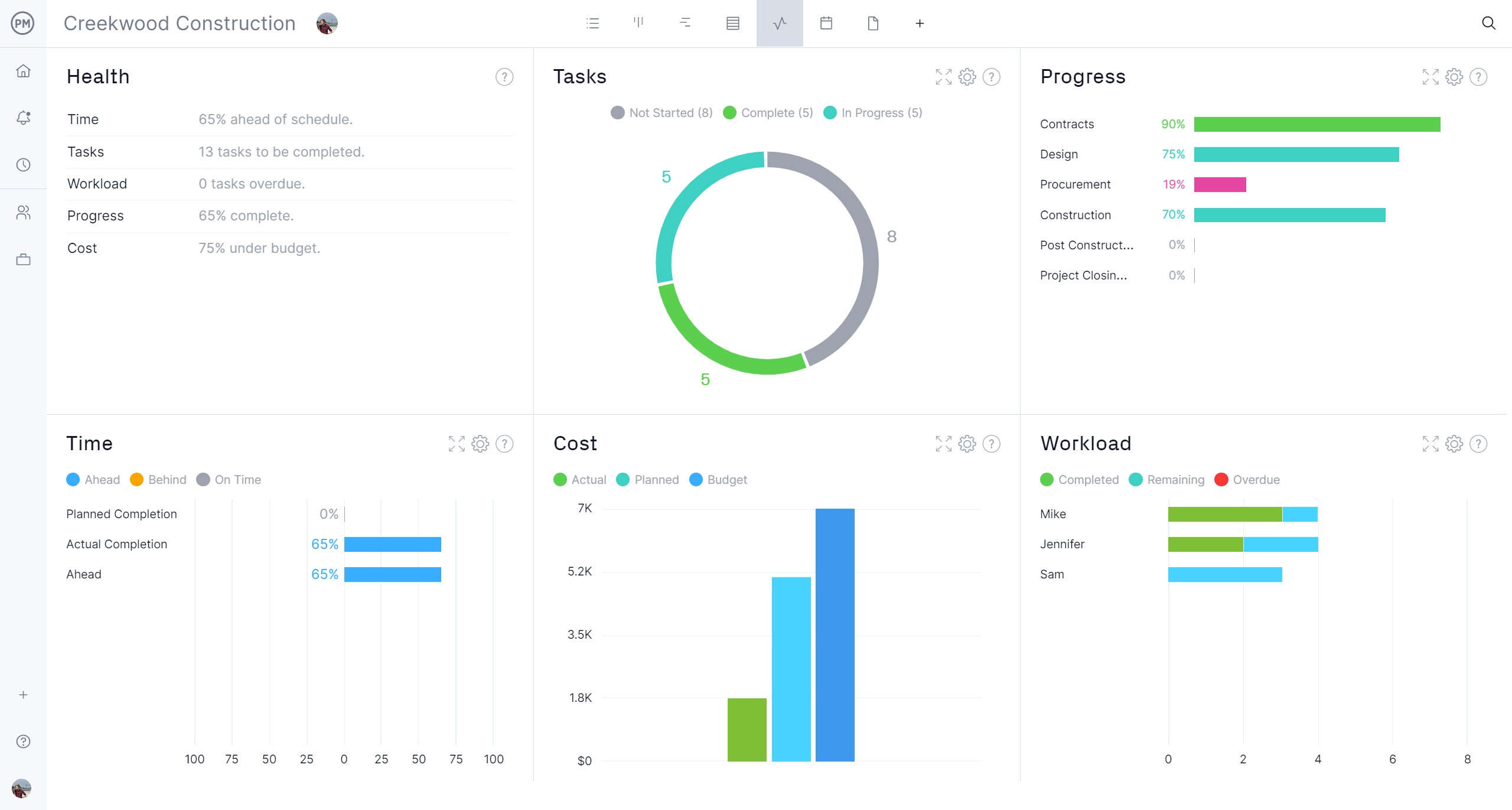
Track Time, Cost and Progress With Real-Time Dashboards
How to manage a project might hinge on tracking. Without monitoring project metrics, the project is blind. To get a high-level overview of progress and performance, toggle to the real-time project or portfolio management dashboards. They automatically collect live data and display it on easy-to-read graphs and charts showing time, cost, workload and more.
Customizable reports go deeper into status, variance, workload, timesheets and more. Each can be filtered to focus on specific data points or more be more general and shared with stakeholders to keep them updated. Even our secure timesheets help track labor costs to keep on budget.

Related Project Management Content
There’s a lot more about how to manage a project than the 10 steps we outlined above. For readers interested in learning about the project life cycle, documentation and more, below are a handful of recently published articles from our blog.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.