Business strategic planning defines an organization’s long-term goals and competitive direction, while project, program and portfolio management execute the initiatives that bring those goals to life. However, these domains can drift apart without alignment. Strategic portfolio management bridges this gap, ensuring that the portfolio of projects and programs reflects strategic priorities and delivers measurable value.
What Is Strategic Portfolio Management?
Strategic portfolio management (SPM) is the process of selecting, prioritizing and managing an organization’s strategic initiatives, projects, programs and investments in alignment with its objectives. It links high-level strategy to day-to-day execution by ensuring resources are directed toward the most impactful and strategically aligned initiatives.
Organizations of all sizes implement SPM, and it’s common in industries like technology, healthcare, finance, manufacturing and government, where resources are limited and priorities shift. Both for-profit businesses and public sector entities use SPM to ensure investments deliver maximum value and support long-term objectives.
Project management software supports strategic portfolio management by giving organizations a centralized way to align projects with business goals, prioritize initiatives and allocate resources effectively across the portfolio. It provides visibility into project performance, risk and capacity, helping leadership make informed decisions about which projects to start, continue or stop. With built-in reporting and real-time data, teams can stay aligned with strategic objectives while adapting quickly to changing business needs.
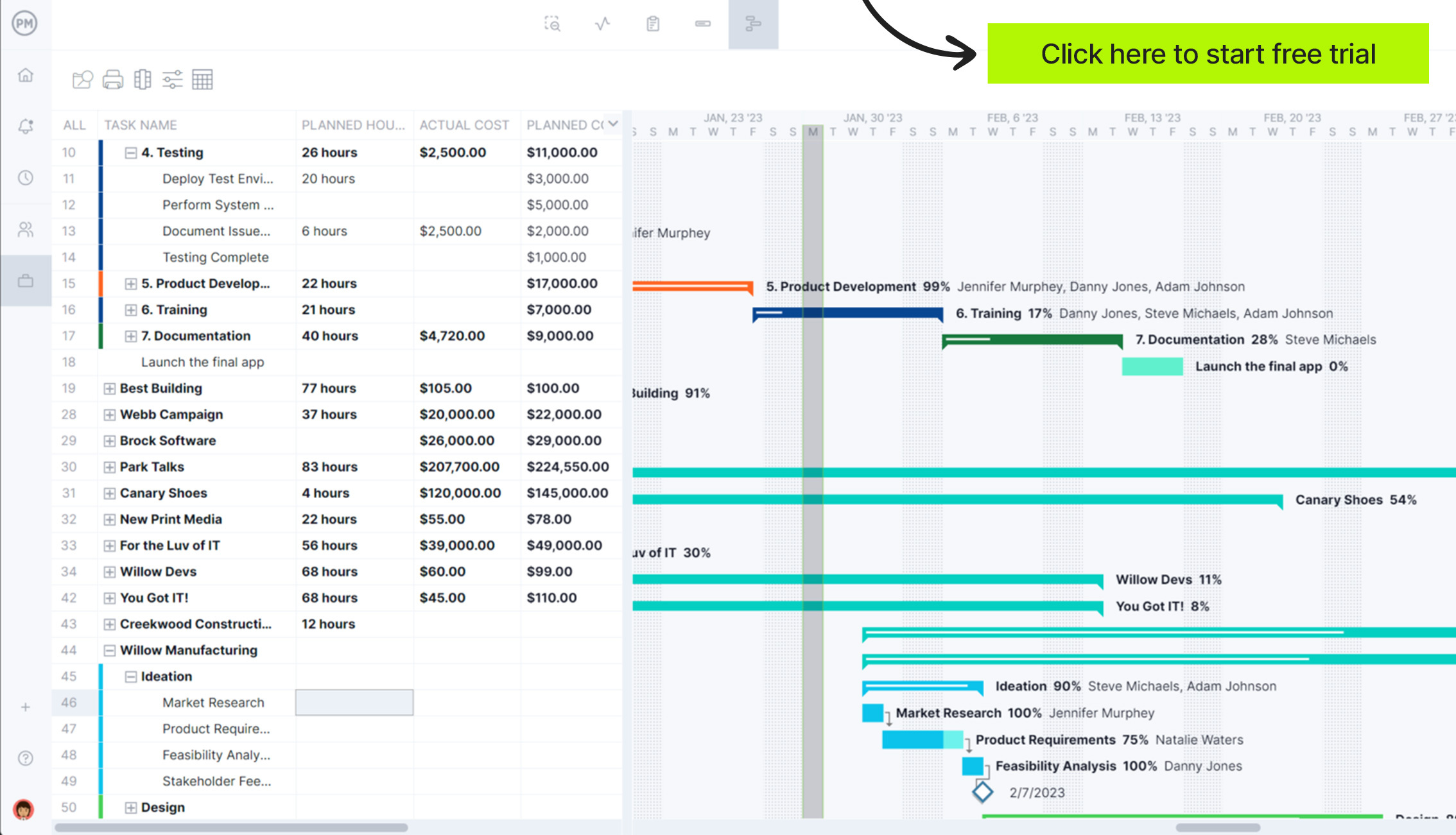
ProjectManager’s roadmap feature enhances strategic portfolio management by offering a high-level, visual timeline of all projects across your portfolio. It shows how individual projects align with broader goals, where they overlap and when key milestones occur. This makes it easier for executives and PMOs to balance workloads, spot scheduling conflicts and ensure resources are directed to the most valuable initiatives—all while keeping the entire organization aligned around long-term strategy.

Key Strategic Portfolio Management Benefits
Strategic portfolio management offers several advantages by aligning initiatives with strategy and optimizing performance. Below are some of the most impactful benefits organizations gain from implementing SPM effectively.
Promotes Resource Efficiency
One core goal of strategic portfolio management is to use organizational resources as effectively as possible. By planning and allocating resources across the entire portfolio, organizations can minimize idle labor and underused equipment.
SPM also enables bulk purchasing of materials and supplies, lowering costs and ensuring teams are consistently working on the most valuable, strategically aligned initiatives without unnecessary duplication or waste.
Facilitates Collaboration Across Business Departments
Strategic portfolio management creates a unified framework that fosters collaboration among teams across various business departments. By aligning all initiatives with strategic objectives, SPM encourages departments like finance, operations, IT and marketing to coordinate their efforts and share resources effectively.
This cross-functional alignment breaks down silos, improves communication and ensures that everyone works toward common goals. The result is more efficient execution of initiatives, better use of organizational knowledge and stronger outcomes driven by collective expertise and shared accountability.
Controls Risk and Maximizes Return on Investment
SPM balances risk and reward by managing the organization’s portfolio in line with its risk tolerance and strategic goals. It provides a structured approach to assess and prioritize initiatives based on their potential returns and associated risks.
By diversifying investments, avoiding over-concentration in risky areas and regularly monitoring threats, SPM mitigates risks while pursuing high-value opportunities. This careful balancing act ensures that resources are invested in initiatives that offer optimal returns without exposing the organization to unnecessary or excessive risk.
Related: Best Project Portfolio Management Software
Strategic Portfolio Management Process
The strategic portfolio management process aligns projects and programs with business goals through a structured sequence of steps. It ensures initiatives are selected, prioritized and executed to deliver maximum value while supporting the organization’s long-term strategy.
1. Identify the Organization’s Strategic Objectives
The first step in the strategic portfolio management process is to analyze the organization’s strategic plan and clearly define its current strategic objectives. This involves understanding the vision, mission and long-term goals, as well as assessing market conditions, competitive positioning and internal capabilities.
By identifying these objectives, decision-makers establish a foundation for evaluating and prioritizing initiatives. It ensures that all portfolio investments directly support the organization’s priorities and create measurable value aligned with its overall business strategy.
Related: 12 Strategic Planning Templates for Excel & Word
2. Define Portfolio Governance Roles and Responsibilities
Project portfolio governance is the framework of policies, processes and decision-making structures that guide how projects and programs are selected, prioritized and managed to align with strategy. It ensures accountability, transparency and alignment across the organization.
- Steering Committee: Oversees the portfolio, sets priorities, resolves conflicts and ensures alignment with strategic goals. Provides guidance and approves major decisions.
- Company Executives: Define strategic direction, approve funding and communicate priorities. Ensure the portfolio supports business objectives and delivers value to stakeholders.
- Department Managers: Manage day-to-day operations within their departments, provide subject-matter expertise and ensure departmental resources are available and aligned to support portfolio initiatives.
- Board of Directors: Provides high-level oversight, ensuring portfolio investments comply with governance standards, legal requirements and shareholder interests.
- Project Portfolio Manager: Coordinates portfolio activities, evaluates initiatives, manages performance metrics and recommends adjustments to maintain alignment with strategy.
- Program Manager: Manages groups of related projects, ensures program-level benefits are realized and maintains alignment with both portfolio and organizational goals.
- Project Portfolio Management Office: Supports governance by providing processes, tools and reporting. Ensures consistency, transparency and best practices across the portfolio.
- Project Manager: Leads individual projects, ensuring they are executed efficiently, meet objectives and contribute to portfolio-level outcomes.
3. Establish a Project Intake Process
In the context of strategic portfolio management, the project intake process is a structured approach to collecting, evaluating and prioritizing proposed projects, programs and strategic initiatives. It ensures that only initiatives aligned with organizational objectives enter the portfolio.
This process involves evaluating business cases, assessing strategic fit, estimating costs and benefits and ranking initiatives based on value and feasibility. By standardizing intake, organizations can avoid ad-hoc decisions, eliminate low-value projects early and maintain focus on high-impact initiatives that support their strategy effectively and efficiently.
4. Balance Risk and Reward for the Portfolio
An essential part of the strategic portfolio management process is balancing the portfolio’s overall risk and reward. This involves analyzing each initiative’s potential benefits, costs and risks to ensure the portfolio aligns with the organization’s risk appetite while maximizing value.
SPM diversifies investments across short- and long-term, high- and low-risk projects to avoid overexposure. It also continuously monitors risks, reallocates resources as needed and adjusts priorities to maintain an optimal balance. This approach helps protect the organization from significant losses while pursuing opportunities that deliver competitive advantage and growth.
See how ProjectManager’s built-in RAID log can help better manage and mitigate project risks, assumptions, issues, dependencies and changes.
5. Approve Portfolio and Allocate Organizational Resources
After completing the project intake process and balancing risk and reward, the next step is to formally approve the portfolio. Decision-makers select the mix of strategic initiatives, projects and programs that best align with organizational goals and deliver maximum value.
Once approved, resources—such as budgets, personnel, equipment and materials—are allocated to each initiative based on priority and need. This ensures that all approved initiatives have the necessary support to proceed efficiently, avoids resource conflicts and aligns execution with strategic intent. Careful allocation also minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization across the organization.
6. Monitor and Review Portfolio Performance
Once the strategic initiatives, projects and programs enter the execution phase, it’s essential to continuously monitor and review their performance. This ensures they remain aligned with strategic goals and deliver expected benefits. Monitoring is a collaborative effort involving department managers, project managers, program managers and the project portfolio manager.
They track progress, measure key performance indicators and assess resource utilization, risks and benefits realization. Regular reviews enable timely adjustments, reallocation of resources or even termination of underperforming initiatives, maintaining the portfolio’s overall health and ensuring it continues to deliver maximum value to the organization.
7. Optimize the Portfolio
Project portfolio optimization is the process of analyzing and adjusting the portfolio to ensure it delivers maximum value within the constraints of budget, resources and strategic goals. It involves reprioritizing, adding, or removing initiatives to maintain alignment with evolving business needs and improve overall portfolio performance.
Optimizing the portfolio is crucial in the SPM process because organizational priorities, market conditions and resources often change over time. Regular optimization ensures that the portfolio remains aligned with strategy, avoids wasted effort on low-value initiatives and continues delivering the highest possible return on investment while minimizing risk.
8. Close the Project Portfolio
Closing the project portfolio involves formally completing all initiatives and ensuring all strategic objectives have been addressed. Key procedures include documenting lessons learned to capture successes, challenges and recommendations for future portfolios.
Final performance reviews are conducted to assess benefits realization and resource utilization. Financials are reconciled, outstanding risks or issues are resolved and all documentation is archived. Stakeholders are informed of the portfolio’s closure and resources are released or reassigned. This step ensures transparency, accountability and continuous improvement by applying insights gained to strengthen future strategic portfolio management efforts.
Strategic Portfolio Management Tools
Strategic portfolio management tools help organizations plan, align and monitor their initiatives effectively. These tools provide structure, visibility and insight to ensure the portfolio delivers maximum value and remains aligned with evolving business strategies and objectives.
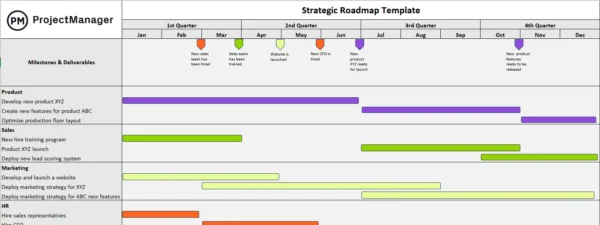
Strategic Roadmap
A strategic roadmap is a visual planning tool that outlines the key initiatives, milestones and timelines needed to achieve long-term business goals. It provides a high-level view of how strategic objectives will be executed over time, helping communicate priorities and progress.
In the SPM process, a strategic roadmap is used to align initiatives with business objectives, set realistic timelines and coordinate cross-functional efforts. It enables stakeholders to see the sequence of initiatives, understand dependencies and adjust plans as needed to maintain strategic alignment and respond to changes effectively.

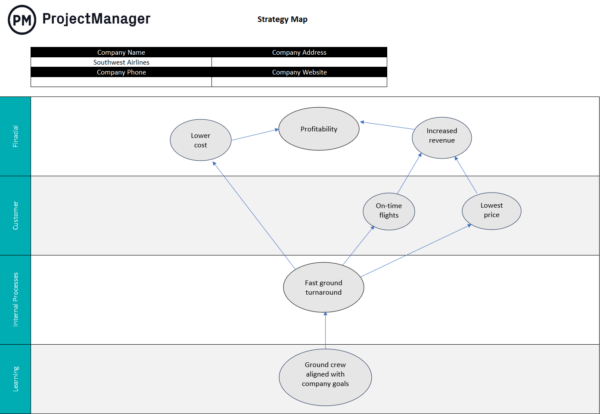
Strategy Map
A strategy map is a visual representation of an organization’s strategic objectives, showing how they interconnect across different perspectives—such as financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth. It helps clarify the cause-and-effect relationships that drive strategic success.
Within the SPM process, a strategy map is used to ensure initiatives are clearly tied to strategic objectives. It helps identify gaps in the portfolio, prioritize initiatives that support key goals and communicate strategy across the organization. This alignment improves decision-making and ensures resources are focused on what matters most.

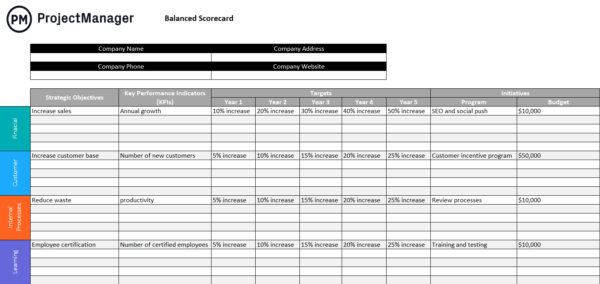
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard is a performance management tool that tracks organizational objectives across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes and learning & growth. It helps measure progress toward strategic goals by combining financial and non-financial metrics, offering a comprehensive view of performance.
In the SPM process, the balanced scorecard is used to monitor how portfolio initiatives contribute to achieving strategic objectives across all perspectives. It provides clear metrics to assess progress, identify gaps and guide decisions, ensuring initiatives remain aligned and deliver balanced, sustainable value over time.

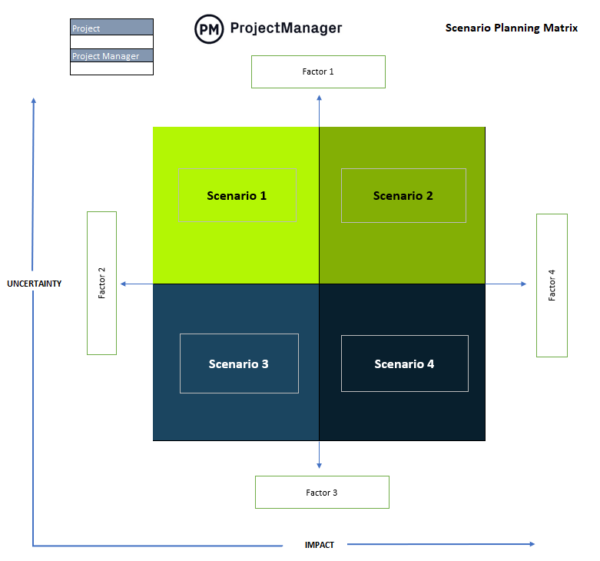
Scenario Planning Matrix
A scenario planning matrix is a strategic tool that explores possible future conditions by analyzing key uncertainties and their impact on objectives. It maps out multiple scenarios to help organizations prepare for different outcomes and make more resilient plans.
In the SPM process, the scenario planning matrix helps evaluate how the portfolio would perform under various potential futures. This insight enables decision-makers to select a mix of initiatives that minimizes risk, capitalizes on opportunities and remains adaptable to changing external factors.

Risk Heat Map
A risk heat map is a visual tool that plots risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. It helps organizations quickly identify, prioritize and monitor risks within the portfolio by categorizing them into low, medium, or high threat levels.
In the SPM process, the risk heat map is used to assess portfolio-level risks, enabling managers to allocate resources for mitigation where needed. It ensures risks are understood, monitored and managed effectively, supporting a balanced portfolio that aligns with the organization’s risk tolerance and strategic objectives.
How ProjectManager Helps with Strategic Portfolio Management
ProjectManager helps organizations manage strategic portfolios more effectively than static templates by offering multiple, real-time project views that support both high-level planning and day-to-day execution. With Gantt charts, kanban boards, task lists and roadmap views all synced in one platform, stakeholders can visualize how each project contributes to strategic goals and make faster, more informed decisions. This flexibility allows teams to work in the format that suits them best while ensuring leadership maintains visibility across the entire portfolio.
Manage Resources Across Projects
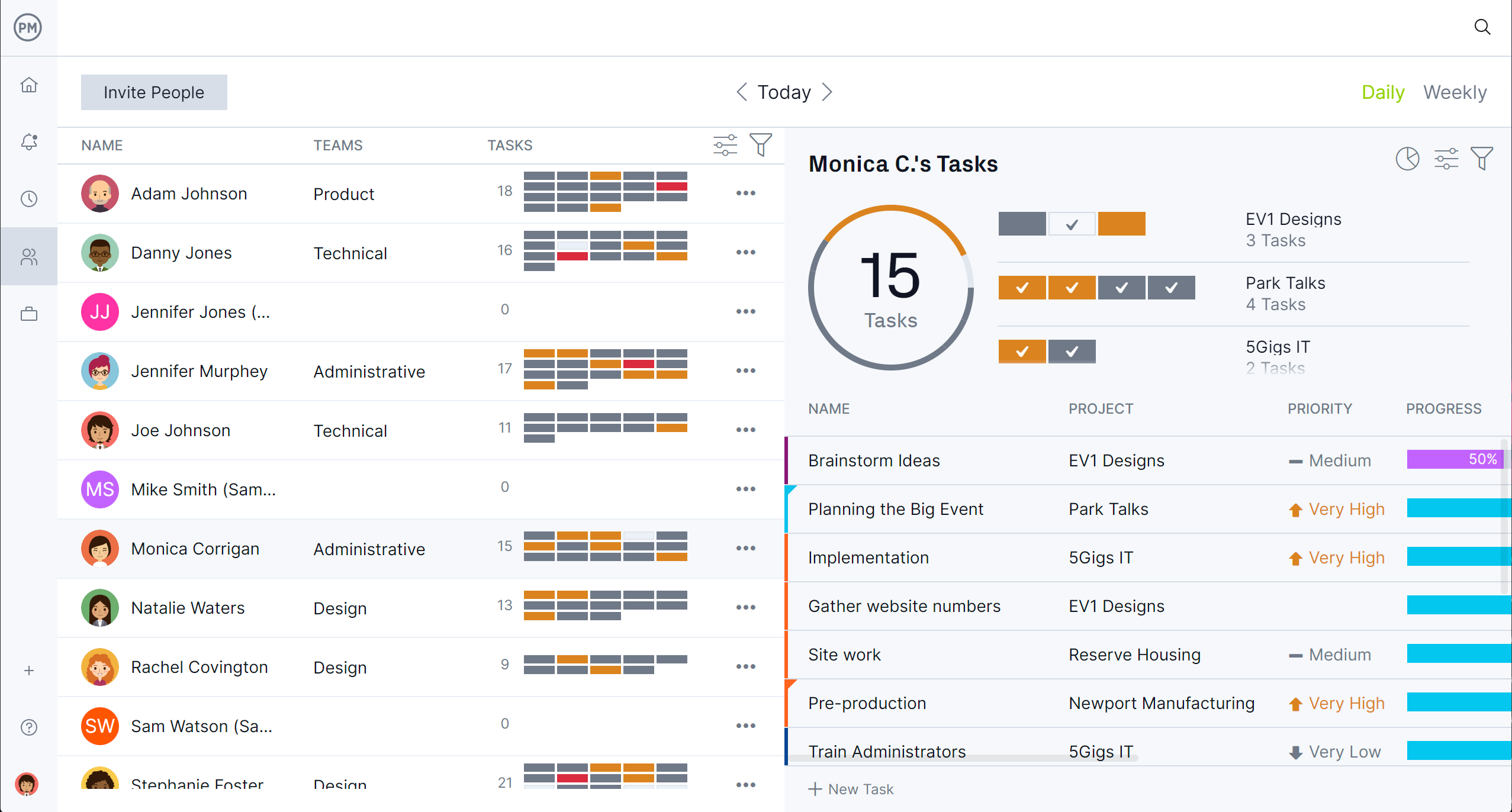
Its built-in resource management tools are essential for portfolio-level planning, giving you a clear view of team availability, workload and allocation across all projects. You can assign work based on capacity, quickly rebalance workloads and identify resource conflicts before they affect delivery.
A team page provides a daily or weekly summary of their activities, which can be filtered by priority or progress and tasks updated without leaving the page. Unlike templates, which require manual tracking, our live data updates ensure your portfolio stays properly staffed and aligned with strategic priorities.
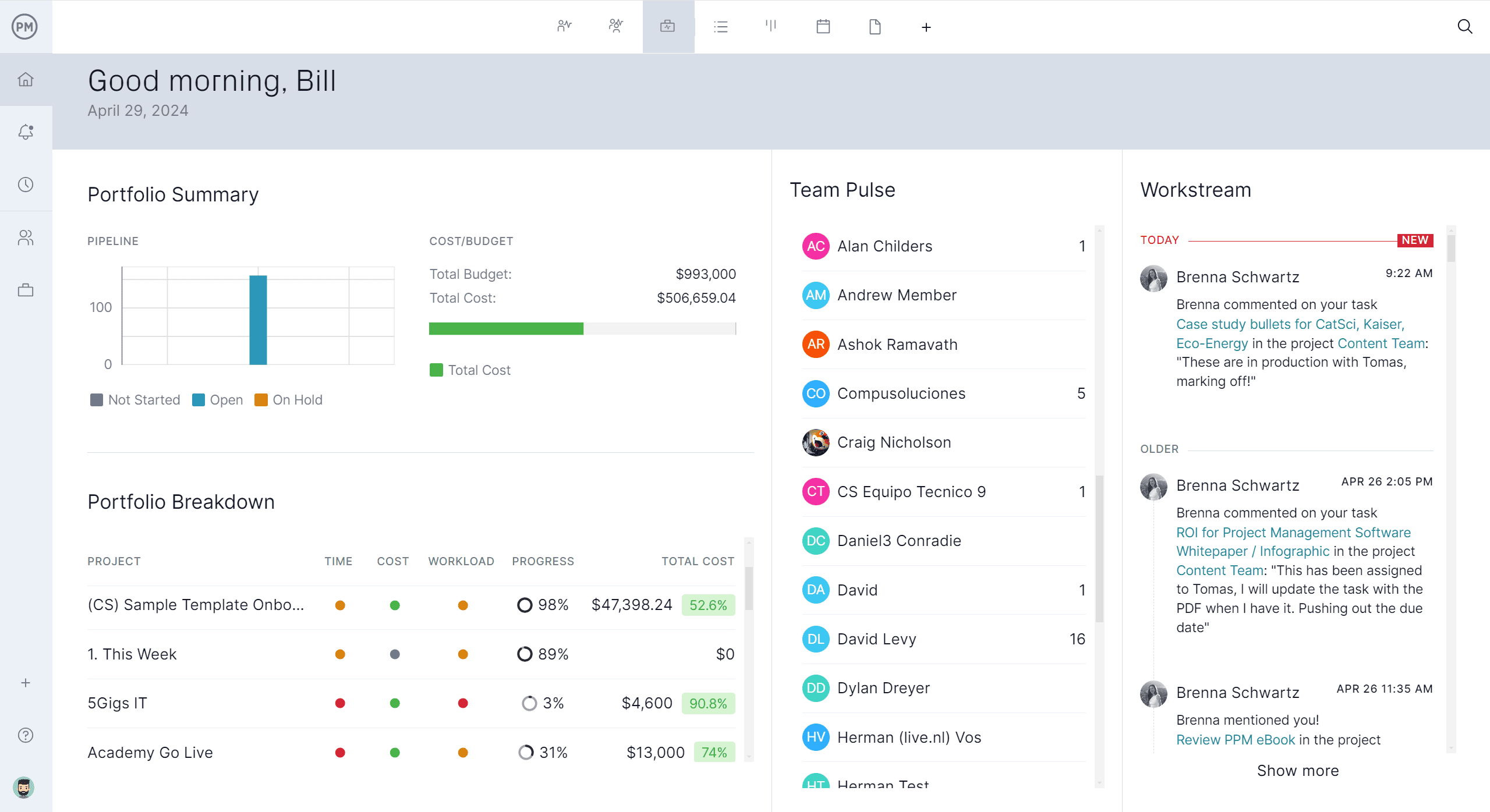
Get Deep Insights Into Portfolio Metrics
Our software also delivers real-time dashboards and customizable reports that provide instant insight into project health, progress, budget and risk across the entire portfolio. Automated updates replace manual data entry, while timeline comparisons and performance metrics help you monitor outcomes against strategic benchmarks.
This level of visibility ensures you can steer the portfolio proactively, spot underperforming projects early and keep everything aligned with your organization’s long-term goals.
Related Project Portfolio Management Content
Strategic portfolio management is part of the larger project portfolio management process. For those that want to learn more about this topic, follow the links below. They lead to roundups of portfolio templates and software as well as much more.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.