In project management, different approaches help organizations achieve their goals based on the nature of the work. This article explores 10 types of project management, providing their definitions, when to use them and their pros and cons. Understanding these methodologies enables businesses to select the most suitable approach for their projects, thereby ensuring success. Each type is suited to particular project characteristics, making it important to evaluate your needs before selecting one.
There are also project management software products designed to facilitate these different types of project management. Some are dedicated to only one way of working, while others can be used for any kind of project. The question is, what is the right software for the project you’re managing? That depends on several factors, including the various tools available, some of which work best with a traditional approach and others that are designed to excel in a more modern mode of working.
ProjectManager is flexible project and portfolio management software that supports a wide range of project types, from waterfall to agile and hybrid approaches. Its customizable tools adapt to different industries, teams and workflows, making it suitable for construction, IT, manufacturing and more. Kanban boards help scrum teams work iteratively and task lists are often used in software development.
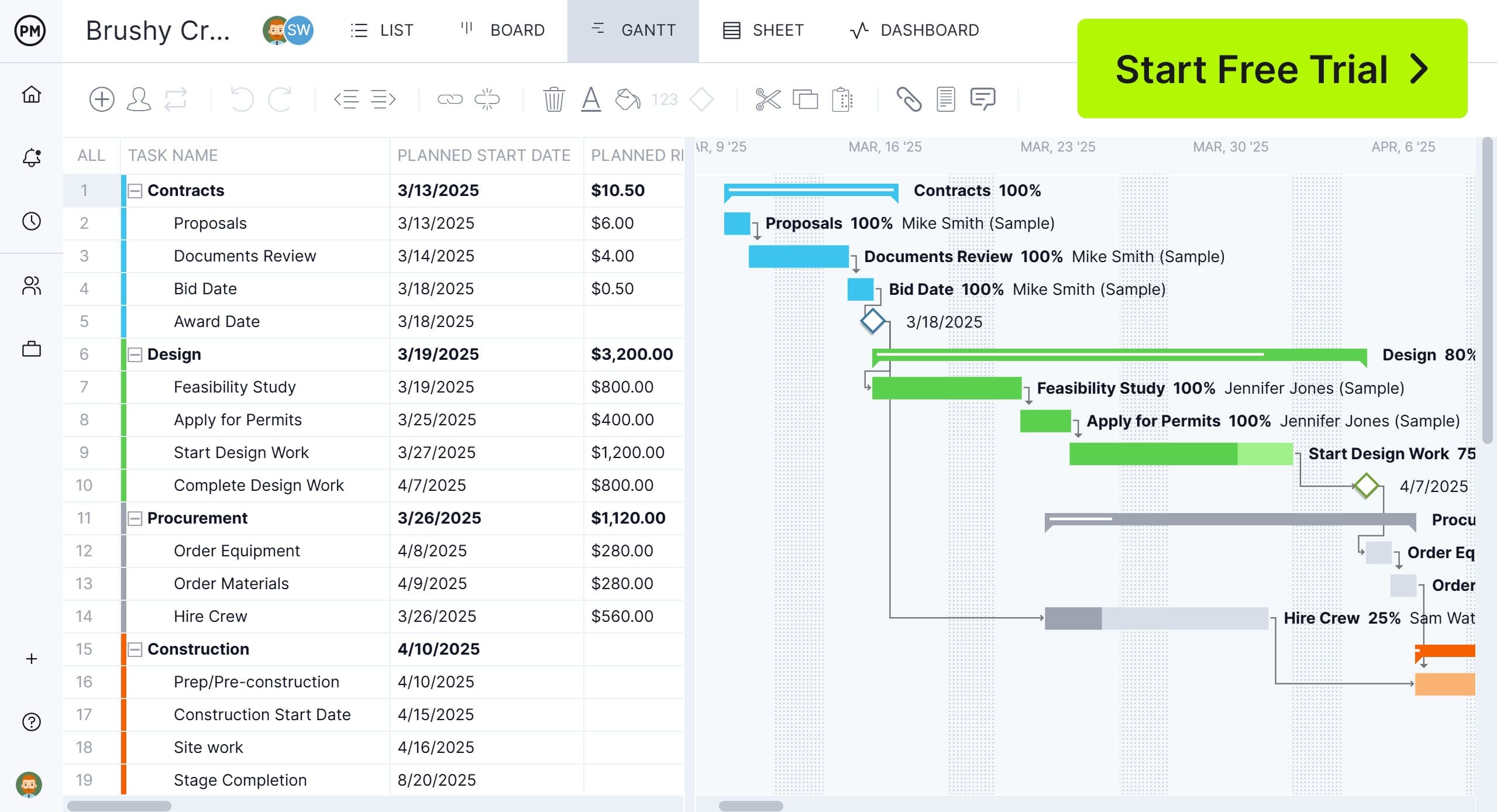
The Gantt chart, which allows users to plan, schedule and track tasks with timelines, dependencies and milestones, is the workhorse of waterfall. It links all four types of task dependencies to avoid cost overruns, filters for the critical path to identify tasks with zero slack and sets a baseline to track progress, cost and more in real time. The interactive chart updates in real time as changes are made, helping teams stay on schedule and aligned with goals while managing complex projects with ease. Plus, it seamlessly integrates with all the other project views for cross-functional teams. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

1. Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall project management is a linear and sequential approach where each phase must be completed before moving to the next. It typically includes stages like planning, design, implementation, testing and maintenance. This method emphasizes thorough documentation and clear deliverables at every step. Waterfall works best when project requirements are well-defined and unlikely to change. Its structured nature makes it easier to manage timelines and budgets, but it can lack flexibility for dynamic or evolving projects.
When to Use Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall project management is ideal for projects with clear, fixed requirements and little expected change. It works well for large or medium-sized projects where each phase can be planned in detail, such as construction, manufacturing or government contracts. The method suits industries with strict regulations or where quality control and documentation are critical. Avoid using it for highly innovative or uncertain projects since its rigid structure makes accommodating changes difficult once the project is underway.
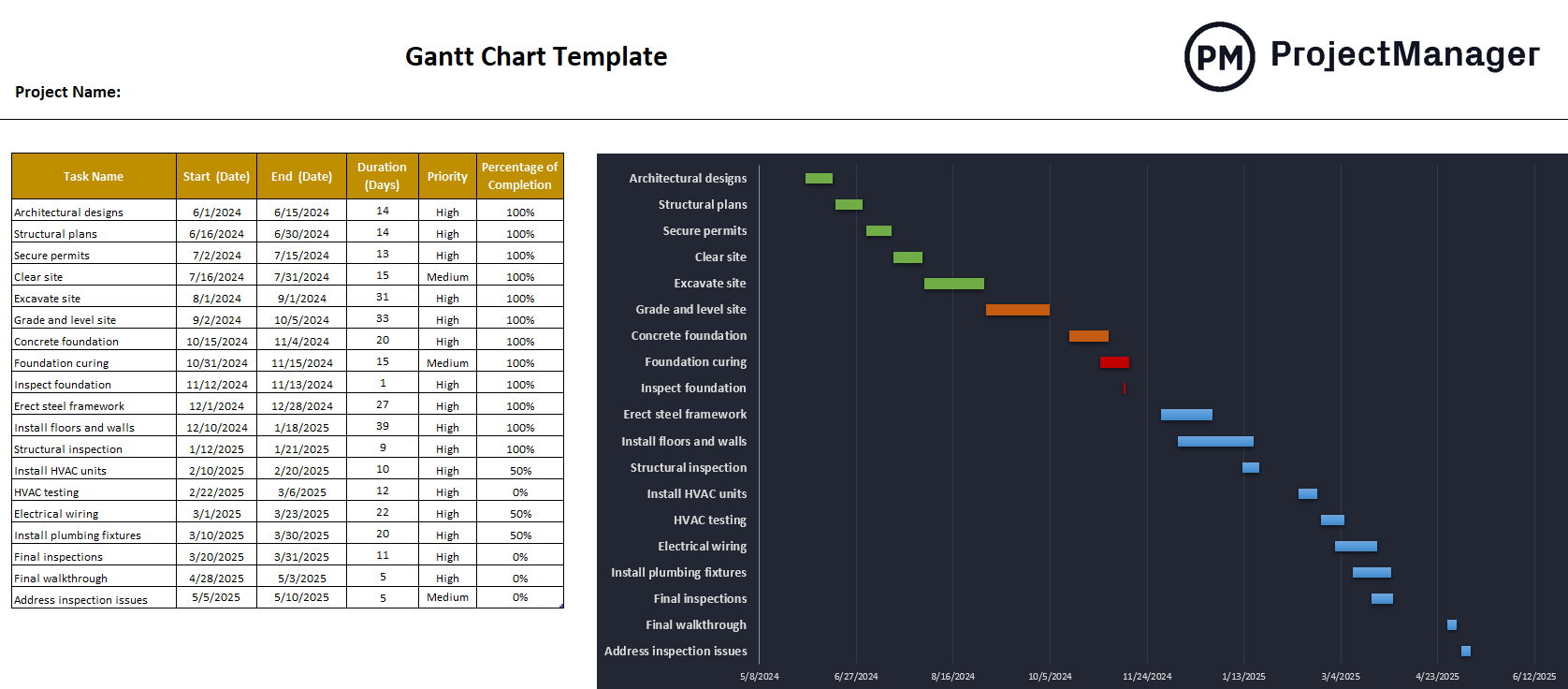
The Gantt chart is the preferred tool for those using the waterfall methodology. Project managers can use it to create and oversee subtasks, dependencies and more during each stage of the project. Download our free Gantt chart template for a streamlined way to keep your project structured.

Pros and Cons of Waterfall Project Management
Before choosing the waterfall approach, it’s important to weigh its advantages and disadvantages. Below, we outline the key pros and cons to help you determine if this structured methodology aligns with your project’s goals and constraints.
Pros of Waterfall Project Management
- Clear structure and defined phases
- Detailed documentation throughout the project
- Easy to track progress against the plan
- Works well for projects with stable requirements
- Facilitates quality control and compliance
Cons of Waterfall Project Management
- Lacks flexibility for changes once started
- Can be inefficient if requirements evolve
- Late discovery of issues during the testing phase
- High risk if the initial requirements are incorrect
- Not suited for innovative or uncertain projects
2. Agile Project Management
Agile project management is an iterative and flexible approach that emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback and small, incremental progress. Teams work in short cycles called sprints, delivering functional components regularly. Agile promotes adaptability to changing requirements and focuses on delivering value quickly. It is less rigid than traditional methods, empowering teams to make decisions and adjust priorities as needed. Agile works best for projects where requirements evolve and customer input plays a significant role in shaping outcomes.


When to Use Agile Project Management
Agile project management is ideal for projects with high uncertainty, evolving requirements or where stakeholder feedback is crucial. It suits industries like software development, marketing and product design, where innovation and speed to market matter. Agile works well for small to medium-sized teams that can collaborate closely and respond quickly to change. It’s also effective for complex projects broken into manageable parts. However, it may not be the best choice for highly regulated industries or projects requiring strict documentation.
Pros and Cons of Agile Project Management
Agile offers many benefits but also has some challenges to consider. Below are the main pros and cons to help you decide if this adaptive methodology aligns with your team’s needs and project goals.
Pros of Agile Project Management
- Flexibility to adapt to changing requirements
- Faster delivery of functional components
- Improved collaboration and team engagement
- Continuous customer feedback throughout the project
- Focus on delivering value early and often
Cons of Agile Project Management
- Requires high customer and team involvement
- Less predictability in scope and timelines
- Can be challenging for large, distributed teams
- Documentation may be less comprehensive
- Not ideal for rigidly regulated industries
Related: Best Project Management Software of 2025
3. Kanban Project Management
Kanban project management is a visual, flow-based method that focuses on managing work as it moves through a process. Tasks are represented on a board, with columns showing stages of completion, such as “To Do,” “In Progress” and “Done.”
Kanban emphasizes limiting work in progress to improve efficiency and prevent bottlenecks. This approach allows teams to visualize tasks, prioritize effectively and adjust dynamically to changing workloads. Kanban is simple, transparent and suitable for continuous delivery environments where flexibility is important.
Related: Free Kanban Board Template
When to Use Kanban Project Management
Kanban project management works best for projects requiring ongoing, continuous delivery without fixed end dates. It suits teams managing repetitive workflows or maintenance tasks, such as in IT operations, support or content production. Kanban is also useful for smaller teams looking to improve efficiency and visibility without overhauling processes. It handles variable workloads and unexpected tasks well, making it ideal for environments with unpredictable demands. However, it may not be ideal for projects requiring strict deadlines or detailed planning.
Pros and Cons of Kanban Project Management
Kanban offers clear benefits and potential drawbacks depending on your project’s needs. Below are the main pros and cons to help you evaluate whether this flexible, visual methodology is right for your team and workflow.
Pros of Kanban Project Management
- Improves workflow visibility and transparency
- Limits work in progress to prevent overload
- Enhances team flexibility and responsiveness
- Works well for ongoing or maintenance tasks
- Easy to implement without major changes
Cons of Kanban Project Management
- Lacks formal structure for complex projects
- Does not define clear deadlines or milestones
- May be less effective for large teams
- Requires discipline to maintain flow limits
- Can become disorganized without regular reviews
4. Critical Path Project Management
Critical path project management is a technique that identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks necessary to complete a project. This sequence, called the critical path, determines the shortest possible duration for the project.
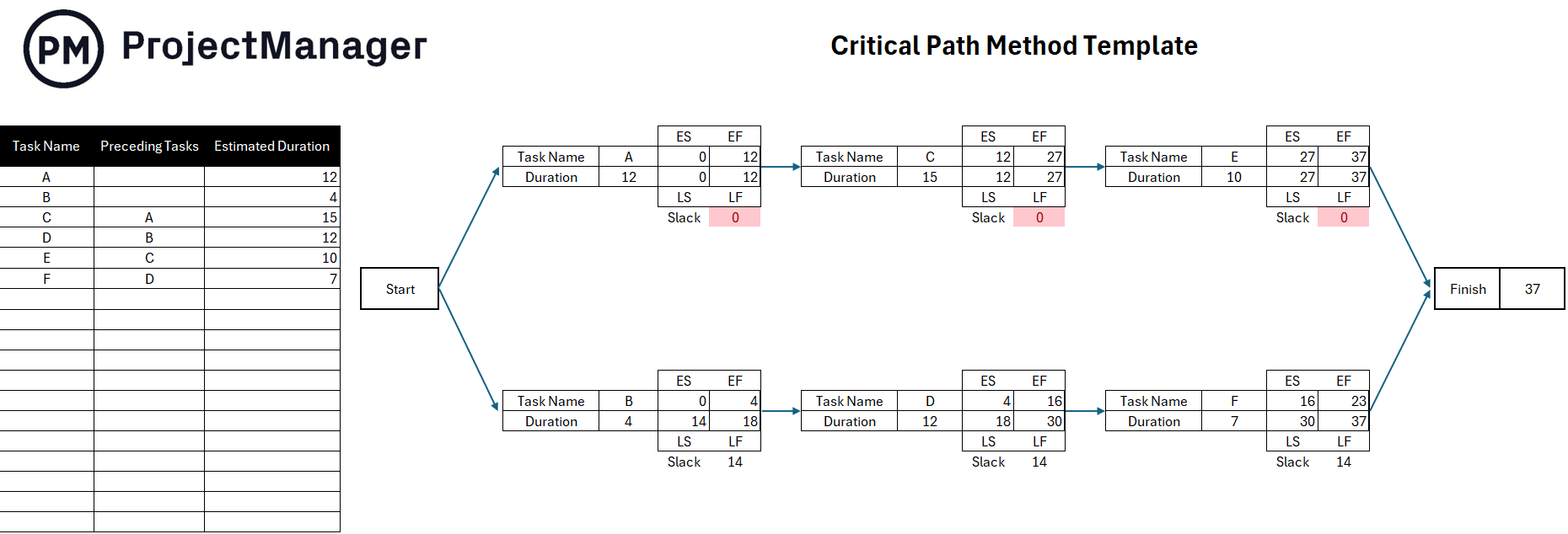

By focusing on critical tasks, project managers can allocate resources efficiently and prevent delays. The method provides clarity on which activities cannot be delayed without affecting the overall timeline. It’s particularly effective for projects with interdependent tasks and tight deadlines that require careful scheduling.
When to Use Critical Path Project Management
Critical path project management is best for large, complex projects with many interdependent tasks and strict deadlines. It suits industries like construction, engineering and event planning, where sequencing activities correctly is crucial. This method works well when the project scope and tasks are clearly defined, and when meeting the final deadline is a priority. It helps teams identify where delays would impact delivery. However, it may not be ideal for highly flexible or creative projects with evolving requirements.
Pros and Cons of Critical Path Project Management
Understanding the pros and cons of critical path methodology helps you determine if its detailed scheduling and focus on dependencies align with your project’s complexity, industry standards and timing needs.
Pros of Critical Path Project Management
- Clarifies task dependencies and project timeline
- Identifies critical tasks that affect delivery
- Helps allocate resources more effectively
- Improves risk awareness and mitigation planning
- Supports meeting tight project deadlines
Cons of Critical Path Project Management
- Requires detailed planning and task definition
- Can become complex for large projects
- Less adaptable to changes during execution
- Focus on the timeline may overlook quality or scope
- Time-consuming to update if the project evolves
5. PRINCE2 Project Management
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a structured, process-driven methodology that divides projects into manageable stages. It emphasizes detailed planning, clear roles and responsibilities and continual business justification. PRINCE2 is highly standardized and includes templates, processes and governance to ensure control and quality. Widely used in the UK and internationally, it’s suitable for projects requiring strong oversight and formal documentation. Its rigorous structure helps organizations maintain alignment with objectives while managing risk effectively and delivering consistent results.

When to Use PRINCE2 Project Management
PRINCE2 is best suited for medium to large projects with complex requirements, significant stakeholders and a need for clear governance. It’s widely used in government, public sector and industries where documentation, compliance and accountability are critical. This method works well when roles need to be clearly defined, and formal reporting is required. PRINCE2 is ideal when projects must adhere to strict processes and standards. However, it may not fit fast-moving projects where flexibility and speed are more important.
Pros and Cons of PRINCE2 Project Management
PRINCE2 has strong benefits and some limitations to consider. Below, we outline the main pros and cons to help you decide if this structured methodology aligns with your project’s needs.
Pros of PRINCE2 Project Management
- Clear roles, responsibilities and governance
- Strong focus on documentation and control
- Ensures projects remain aligned with objectives
- Widely recognized and standardized methodology
- Scalable for different project sizes and types
Cons of PRINCE2 Project Management
- Can be overly bureaucratic for small projects
- Less flexible in dynamic or creative environments
- Requires training to implement effectively
- Documentation can become time-consuming
- May slow progress if applied too rigidly
6. Critical Chain Project Management
Critical chain project management (CCPM) focuses on managing resources and task dependencies to ensure projects are completed on time. Unlike the critical path method, CCPM adds buffers to account for uncertainties and delays, helping teams maintain momentum and avoid multitasking. This method emphasizes keeping resources focused on one task at a time and minimizing idle time. It’s particularly effective for reducing project duration and increasing reliability in delivery by addressing both task dependencies and human resource constraints.

When to Use Critical Chain Project Management
Critical chain project management is ideal for projects where resource availability is a key constraint and schedules are tight. It suits industries like manufacturing, construction and engineering where tasks depend heavily on specific resources. CCPM works well when minimizing delays and improving predictability are priorities. This method is effective for medium to large projects that can benefit from buffer management and resource optimization. However, it may not suit projects with highly flexible requirements or those needing frequent scope changes.
Pros and Cons of Critical Chain Project Management
Critical chain offers notable advantages and some challenges. Below, we summarize its main pros and cons to help you determine if this resource-focused methodology aligns with your project goals.
Pros of Critical Chain Project Management
- Improves resource utilization and efficiency
- Adds buffers to absorb delays and uncertainties
- Reduces project duration by minimizing multitasking
- Increases the predictability of project timelines
- Focuses the team on critical activities and priorities
Cons of Critical Chain Project Management
- Requires cultural change and team buy-in
- Can be complex to plan and implement
- Not ideal for projects with evolving scope
- May overlook non-resource-related risks
- Needs disciplined buffer management to be effective
7. Rapid Application Development Project Management
Rapid application development (RAD) project management is an adaptive approach focused on quickly developing and iterating software through prototypes and user feedback. It prioritizes speed, flexibility and collaboration over detailed planning. RAD emphasizes building working models early and refining them based on stakeholder input. This method allows teams to respond to changing requirements effectively and deliver functional products faster. It’s particularly suited to environments where time-to-market and user satisfaction are critical, and where requirements may not be fully known upfront.

When to Use Rapid Application Development Project Management
RAD project management is ideal for projects with tight deadlines, unclear requirements or the need for frequent user input. It’s commonly used in software development, web design and digital products where quick iterations improve outcomes. RAD suits small to medium-sized teams that can work closely with stakeholders and deliver prototypes rapidly. It works best when the project scope is flexible and users are available to provide continuous feedback. However, it may not suit large, highly regulated or documentation-heavy projects.
Pros and Cons of Rapid Application Development Project Management
RAD offers significant advantages but also presents some limitations. Below, we summarize the pros and cons to help you decide if this fast-paced methodology is right for your project.
Pros of Rapid Application Development (RAD) Project Management
- Faster delivery through iterative development
- Improved alignment with user needs
- Encourages stakeholder collaboration and feedback
- Flexible and adaptable to changing requirements
- Early detection of issues through prototypes
Cons of Rapid Application Development (RAD) Project Management
- Requires active stakeholder participation
- Not suitable for large, complex projects
- May lack comprehensive documentation
- Can be resource-intensive and costly
- Relies heavily on skilled, experienced teams
8. Six Sigma Project Management
Six Sigma project management is a data-driven methodology focused on improving processes by eliminating defects and reducing variability. It combines statistical analysis, quality management and structured problem-solving techniques to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction. Six Sigma uses defined phases—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control (DMAIC)—to ensure projects deliver measurable results. This approach is highly disciplined, emphasizing precision and consistency. It’s particularly effective in organizations where process optimization, cost reduction and high-quality outcomes are critical to success and competitiveness.
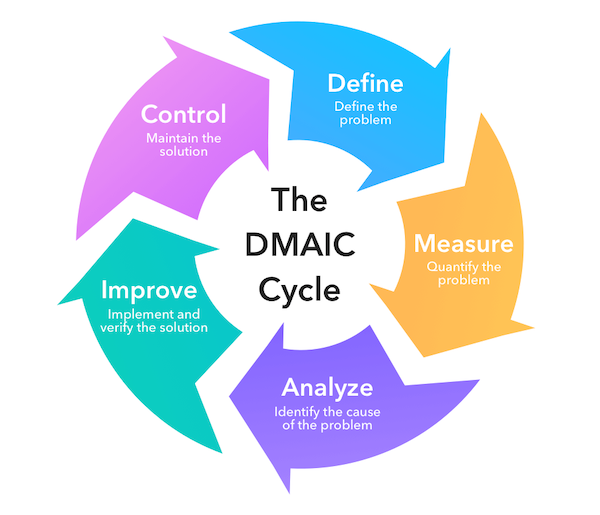

When to Use Six Sigma Project Management
Six Sigma is best for projects aimed at improving existing processes, reducing errors or enhancing product quality. It suits industries like manufacturing, healthcare, finance and logistics where minimizing defects and increasing efficiency are key. Six Sigma works well for medium-to-large projects that can benefit from detailed measurement and analysis. It’s ideal when clear metrics and data-driven decisions are required. However, it may not suit projects with high creativity, rapidly changing scope or minimal measurable outputs.
Pros and Cons of Six Sigma Project Management
Six Sigma offers clear benefits but also has drawbacks to consider. Below are its main pros and cons to help you decide if this rigorous methodology aligns with your project’s goals.
Pros of Six Sigma Project Management
- Reduces errors and process variability
- Improves customer satisfaction and quality
- Provides measurable, data-driven results
- Enhances efficiency and lowers costs
- Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
Cons of Six Sigma Project Management
- Requires extensive training and expertise
- Can be time-consuming to implement fully
- May be too rigid for creative projects
- Focus on metrics can overlook broader goals
- Implementation costs can be high initially
9. Lean Project Management
Lean project management is a methodology focused on maximizing value by eliminating waste and improving efficiency. It emphasizes continuous improvement, respect for people and delivering only what the customer truly needs. Lean encourages teams to streamline processes, reduce unnecessary steps and focus on quality. This approach relies on collaboration, transparency and problem-solving at all levels. Lean is particularly effective in environments where efficiency, speed and customer value are priorities and where minimizing resources without sacrificing quality is essential.

When to Use Lean Project Management
Lean is best for projects that benefit from reduced waste, increased efficiency and customer-centric outcomes. It’s ideal in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, software development and logistics where process optimization delivers significant value. Lean works well for projects where teams can identify and eliminate bottlenecks and improve workflows. It suits organizations committed to continuous improvement and empowering employees. However, it may not fit projects with rigid procedures, little room for flexibility or where change is difficult to implement.
Pros and Cons of Lean Project Management
Lean has many advantages but also some potential drawbacks. Below, we outline its main pros and cons to help you assess if this streamlined methodology aligns with your project’s objectives.
Pros of Lean Project Management
- Eliminates waste and improves efficiency
- Focuses on delivering customer value
- Encourages continuous improvement and learning
- Empowers teams and fosters collaboration
- Improves process transparency and accountability
Cons of Lean Project Management
- Requires cultural change and staff buy-in
- May struggle in rigid, regulated environments
- Can overlook long-term strategy for short-term gains
- Challenging to sustain improvements over time
- Needs ongoing monitoring to prevent backsliding
Related: 38 Project Management Excel Templates and Spreadsheets for Free
10. Hybrid Project Management
Hybrid project management combines elements from different methodologies, such as waterfall and agile, to create a customized approach that suits specific project needs. It allows teams to benefit from the structure of traditional methods while embracing the flexibility of iterative practices. Hybrid adapts to diverse stakeholder expectations and project environments, offering a balance between control and adaptability. This approach is especially useful when no single methodology fully addresses the project’s requirements, enabling managers to tailor processes for optimal results.

When to Use Hybrid Project Management
Hybrid project management is ideal for projects that require both predictability and flexibility. It suits industries like software development, construction and marketing, where some aspects benefit from strict planning while others need adaptability. This approach works well for medium-to-large projects involving multiple teams or stakeholders with varied priorities. Hybrid is effective when integrating agile innovation with waterfall’s discipline. However, it may not fit projects needing strict adherence to a single methodology or with very rigid constraints.
Pros and Cons of Hybrid Project Management
Hybrid offers unique advantages and some trade-offs. Below are the main pros and cons to help you decide if this blended approach aligns with your team’s needs and your project’s goals.
Pros of Hybrid Project Management
- Combines structure and flexibility effectively
- Customizable to fit specific project requirements
- Balances stakeholder needs and team workflows
- Improves collaboration across diverse teams
- Leverages the strengths of multiple methodologies
Cons of Hybrid Project Management
- Requires careful planning to integrate methods
- Can create confusion if not managed properly
- May increase complexity and overhead
- Needs experienced managers to execute well
- Risk of inconsistency if not monitored closely
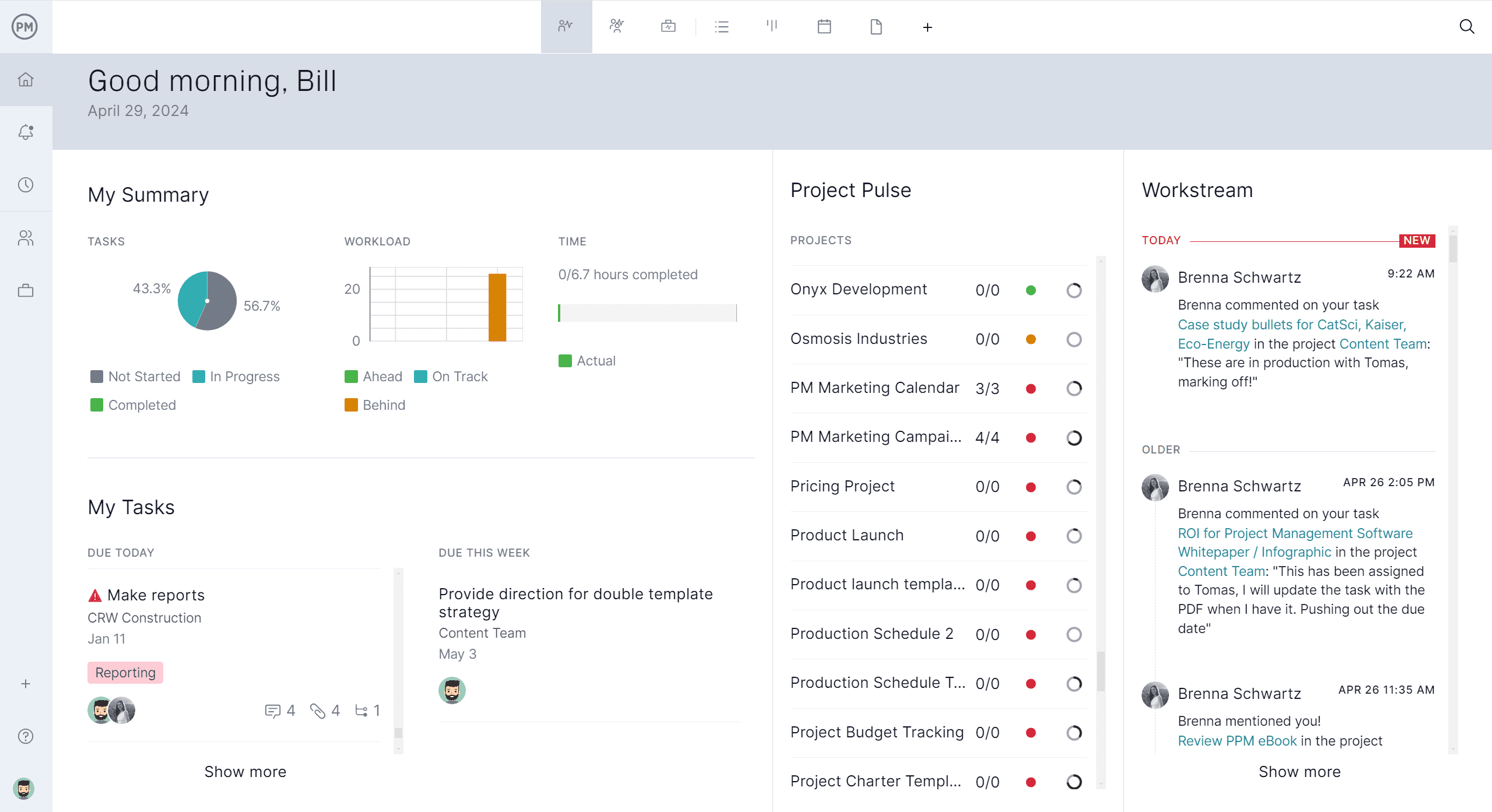
ProjectManager Works for All Types of Project Management
ProjectManager works for all types of project management by offering multiple project views that support different workflows and team preferences. The kanban view helps agile teams by allowing them to manage their backlog, plan sprints and visualize work stages, plus track progress through customizable columns that show task movement. Task lists provide a structured way to manage to-dos and priorities, making it easy to stay organized and focused.
The calendar view lays out tasks by due dates so teams can see what’s coming and manage time effectively. The sheet view resembles a spreadsheet, ideal for users who prefer working with rows and columns to sort and filter data. The Gantt chart adds timeline planning for more complex projects, giving teams the flexibility to manage any project their way.
Effective Resource Management Across All Types of Project Management
Our resource management tools help manage all types of project management by giving teams the ability to balance workloads and plan effectively across any methodology. Availability settings ensure schedules are based on real working hours, so tasks are assigned realistically.
The workload chart shows how tasks are distributed among team members, making it easy to spot imbalances and adjust assignments before they impact progress. The team page centralizes key information like roles, responsibilities and task loads so managers can quickly see who is doing what and allocate resources where they are needed most to keep any project on track.

Track Project Metrics in Real Time With Dashboards, Reports and Timesheets
Use real-time dashboards, customizable reports and secure timesheets to help manage all types of project management by delivering up-to-date insights and accountability across any workflow. Dashboards give instant visibility into progress, performance and resource use so teams can respond quickly to changes.
Customizable reports let users drill into specific metrics like task status costs or workload to support better planning and decision-making. Secure timesheets track actual hours worked, allowing for accurate payroll cost control and compliance while keeping team members accountable. Together, these tools provide the visibility, flexibility and control needed to manage any project efficiently.
Related Project Management Content
There are many types of project management and one blog is not sufficient to do more than superficially touch on the topic. For those who are curious to learn more, follow the links below to recently published articles on project phases, certifications, knowledge areas, principles and much more.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects in all types of project management. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.