VMware: A Milestone Toward the Future of IT Infrastructure
The IT Revolution with Virtualization Technology
In an era where information technology is rapidly advancing, efficiently managing IT infrastructure while reducing costs has become a key challenge for organizations of all sizes. Founded in 1998, VMware has emerged as a leader in Virtualization and Cloud Computing, revolutionizing the way organizations manage and utilize IT resources.
To understand VMware’s significance, we must begin by looking at the fundamental problems organizations faced in the past. Before the era of Virtualization, organizations had to use separate physical servers for each application. This led to inefficient resource utilization, higher costs for hardware, space, and power, as well as complex system management.
VMware addressed these issues with Virtualization technology, enabling organizations to use hardware resources more efficiently, reduce operational costs, and increase flexibility in managing IT systems. Moreover, it has laid the foundation for today’s transition into Cloud Computing.
The Essence of VMware and Its Importance for IT Professionals
VMware is a leading Virtualization and Cloud Computing platform that allows organizations to create and manage multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single physical server. This technology not only saves costs, space, and resources but also drives overall IT system efficiency.
For IT professionals, understanding VMware is an essential skill, as it has become a global industry standard. Knowledge and experience with VMware not only enhance career opportunities but also enable professionals to design, plan, and manage modern, efficient IT infrastructure.
The main benefits of VMware for organizations can be summarized as follows:
1. Cost Savings – By replacing multiple physical servers with Virtual Machines, organizations can significantly reduce hardware expenses, power consumption, and storage requirements.
2. Resource Efficiency – A single physical server can be fully utilized by hosting multiple Virtual Machines simultaneously.
3. Flexibility – Virtualization simplifies backup, migration, and business continuity management, making them faster and more reliable.
An In-Depth Look at VMware Architecture
Understanding VMware’s architecture is crucial for effectively implementing the technology. VMware systems consist of several key components working seamlessly together to create a comprehensive and efficient management environment.
VMware ESXi: The Core of Virtualization
VMware ESXi is a Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-Metal Hypervisor) that installs and runs directly on server hardware without requiring a host operating system. This makes ESXi highly efficient with optimal resource usage.
The difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisors is important to grasp:
Type 1 Hypervisors (e.g., ESXi) run directly on hardware, delivering high performance and reliability—ideal for Data Centers.
Type 2 Hypervisors (e.g., VMware Workstation) run on top of an existing operating system, suitable for testing and personal use.
ESXi’s primary role is to create and manage Virtual Machines, acting as a bridge between physical hardware and the guest operating systems. It allocates CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources to each Virtual Machine as needed.
vSphere Client: A User-Friendly Management Tool
The vSphere Client is a graphical interface (GUI) designed to help administrators easily manage ESXi hosts and Virtual Machines. With its intuitive interface, it provides real-time monitoring and full operational control.
Key functions include:
Creating, editing, and managing VMs.
Monitoring system performance and resource usage.
Configuring security settings and performing maintenance.
Additionally, vSphere Client generates reports and usage statistics, helping administrators analyze trends, plan expansions, and make strategic decisions.
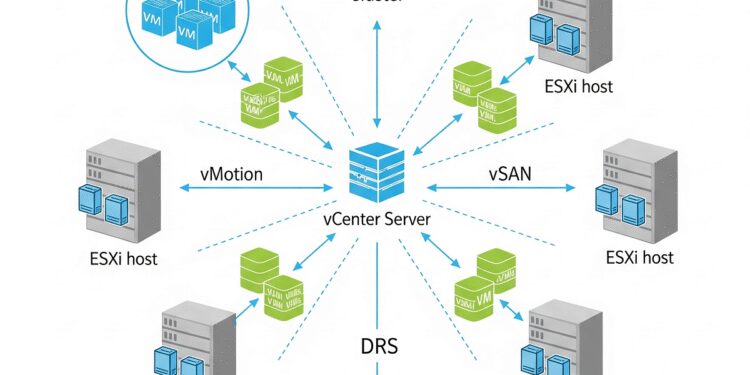
vCenter Server: The Centralized Management Hub
vCenter Server is the central management platform that enables administrators to manage multiple ESXi hosts and Virtual Machines from a single point. This is critical for large organizations with complex infrastructures.
Key features include:
Centralized management of hundreds of ESXi hosts.
VM templates and cloning for rapid deployment.
User permissions and role-based access control for security.
Advanced reporting and analytics for planning and decision-making.
It also integrates with VMware features such as High Availability (HA), Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), and vMotion.
vSAN (Virtual SAN): Revolutionizing Storage
vSAN aggregates local storage from multiple ESXi hosts into a single shared datastore with high performance and reliability.
Key benefits include:
Simplified storage management.
Lower costs by eliminating the need for traditional storage arrays.
Software-defined storage with flexible scaling and maintenance.
vSAN distributes and replicates data across hosts to prevent data loss from hardware failures. It also supports Storage Policies for defining protection levels, performance, and compression per application.
vMotion: Live Migration with Zero Downtime
vMotion is one of VMware’s most innovative features, allowing administrators to migrate running Virtual Machines from one ESXi host to another with zero downtime.
Its importance for Business Continuity is invaluable—administrators can perform hardware maintenance, upgrades, or issue resolution without service interruption.
The process involves copying the VM’s memory state to the destination host, synchronizing changes, and completing the switchover within seconds, so users never notice the migration.
Clusters: Pooling Power for Maximum Efficiency
A Cluster combines multiple ESXi hosts into a single resource pool, offering benefits like:
Automatic failover
Load balancing
Shared resource utilization
If a host fails, VMs are automatically restarted on other hosts in the cluster, minimizing downtime. Clusters also support Resource Pools and Admission Control to ensure failover capacity is always available.
DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler): Automated Resource Balancing
DRS works with clusters to automatically balance workloads across ESXi hosts. Using advanced algorithms, it detects imbalances and migrates VMs with vMotion to optimize resource use.
Benefits include:
Improved performance and stability.
Reduced downtime.
Energy savings with Power Management, which powers down unused hosts during low-demand periods.
vRealize Automation (VRA): Advanced IT Automation
vRealize Automation (VRA) automates VM provisioning and hybrid/multi-cloud management.
Key capabilities:
Self-Service Portal for users to request IT resources.
Blueprints for standardized deployments.
Full lifecycle management of VMs.
Integration with Identity Management for access control.
Cost control via quotas, approval workflows, and policy enforcement.
Impacts and Benefits of VMware in Organizations
VMware adoption represents more than just a tech upgrade—it transforms IT strategies and operations across financial, operational, and competitive dimensions.
Cost Efficiency: An organization running 20 physical servers for applications can often reduce that number to just 3–5 after virtualization. Savings come not only from reduced hardware but also from power, cooling, space, and maintenance costs.
Operational Efficiency: New systems can be deployed in hours instead of weeks. Backup and recovery become more reliable. Large infrastructures can be managed with smaller IT teams.
Flexibility & Agility: Businesses can scale IT resources quickly, test software without disrupting production, and implement robust disaster recovery plans.
Cloud & DevOps Foundation: VMware provides the backbone for cloud migration and DevOps adoption, enabling faster application development, deployment, and adaptability.
Conclusion and Recommendations for VMware Skill Development
VMware has proven to be more than just a virtualization tool—it is a comprehensive platform for building and managing modern IT infrastructure. For IT professionals, VMware expertise is no longer optional but essential.
Recommendations for learners:
1. Start with fundamentals: Understand virtualization concepts, the role of hypervisors, and the benefits of VMware.
2. Hands-on practice: Build lab environments with ESXi, vSphere Client, and vCenter Server to gain practical experience.
3. Advance step-by-step: Explore storage, networking, and security in virtual environments before moving to advanced topics.
4. Expand knowledge: Learn related areas such as Hybrid/Multi-cloud, Containers, Automation, and Infrastructure as Code.
5. Certifications: Achieving VMware certifications like VCP (VMware Certified Professional) or VCAP (VMware Certified Advanced Professional) validates expertise and opens new career opportunities.
In today’s fast-changing technology landscape, VMware remains central to building sustainable, modern IT infrastructure. Investing time and effort into mastering VMware is a worthwhile investment for any IT professional aiming to advance their career and shape the future of information technology.
Above all, continuous learning is vital. Keeping up with VMware’s innovations and related technologies ensures long-term success in IT, where adaptability and growth are the keys to thriving in an ever-evolving industry.